Response of the erosion and siltation in the planning port area in the Tongzhou Bay to storm surges induced by typhoons
-
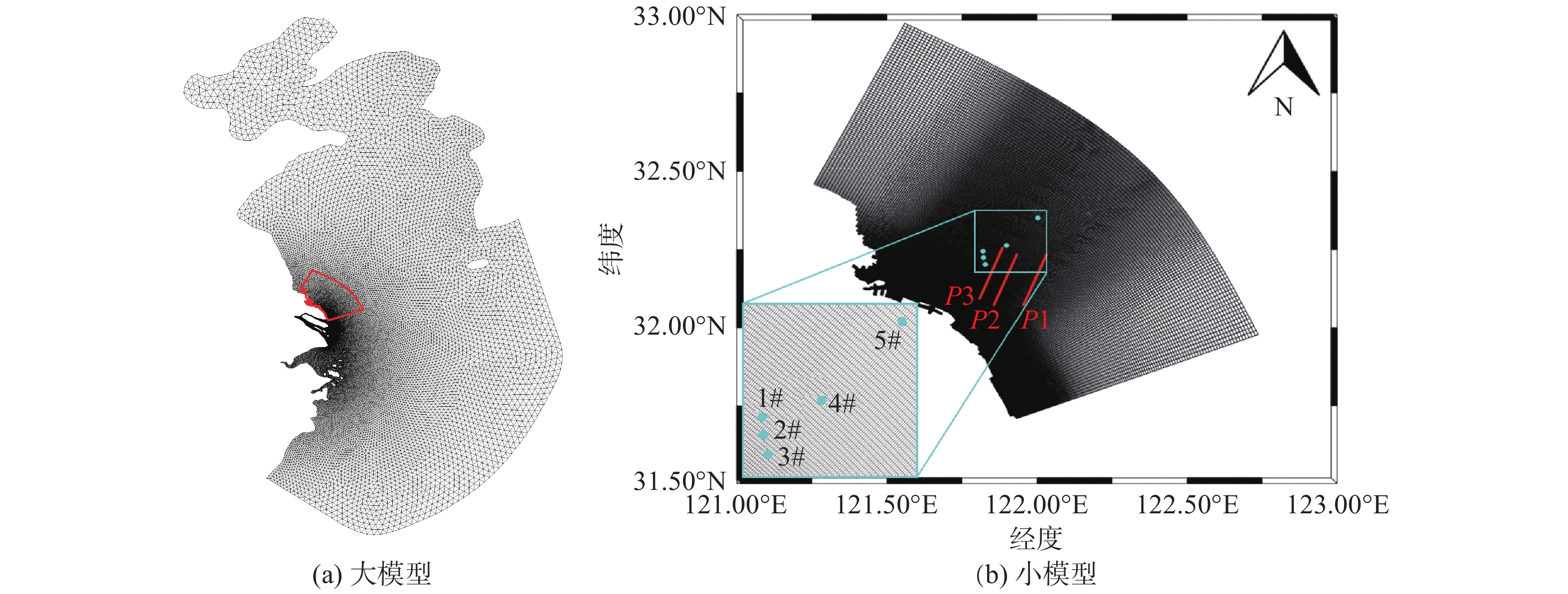
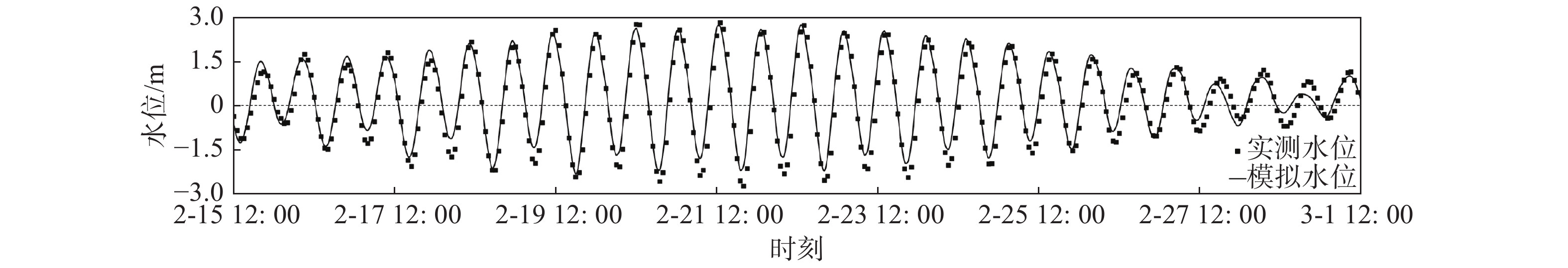
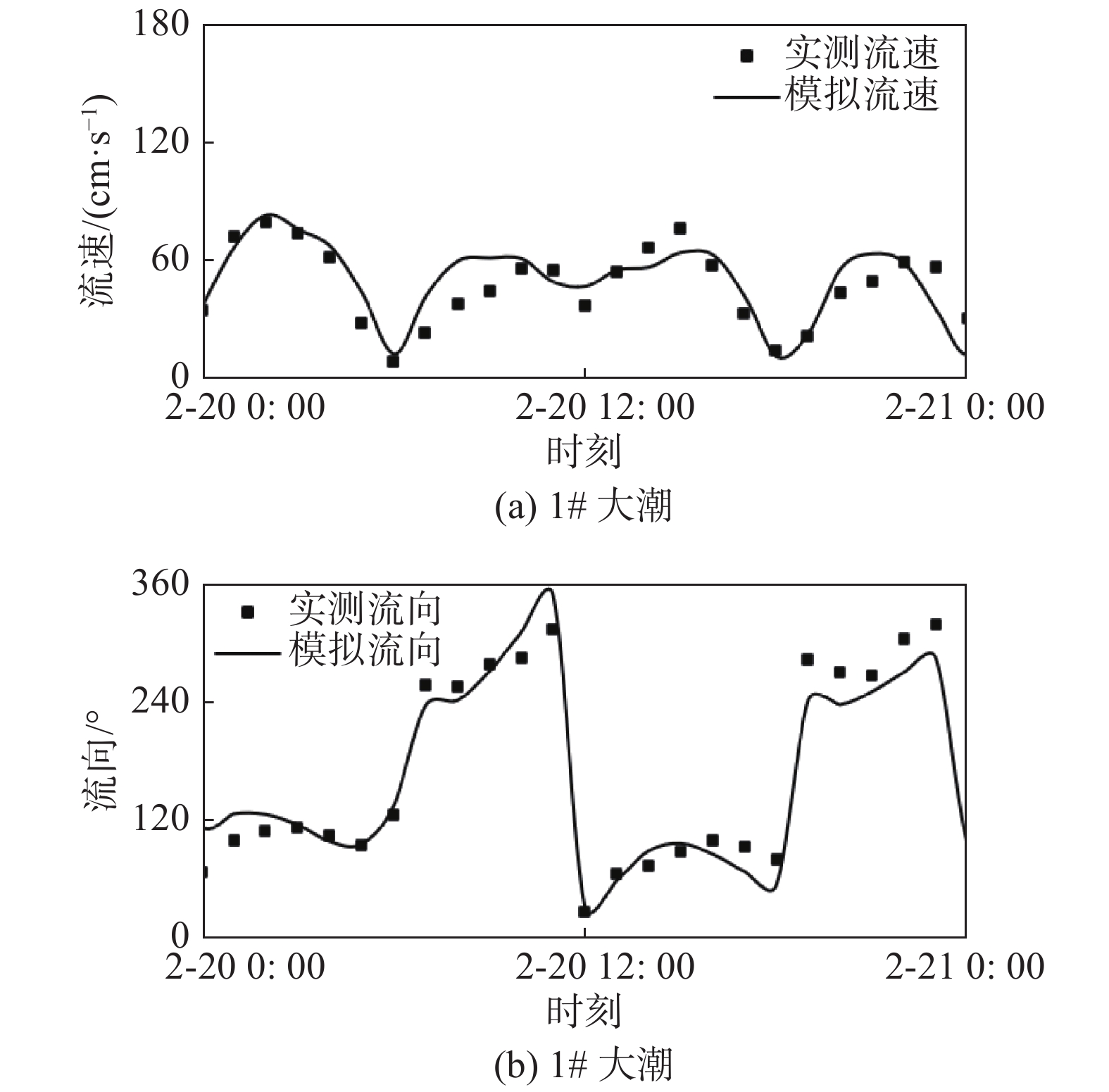
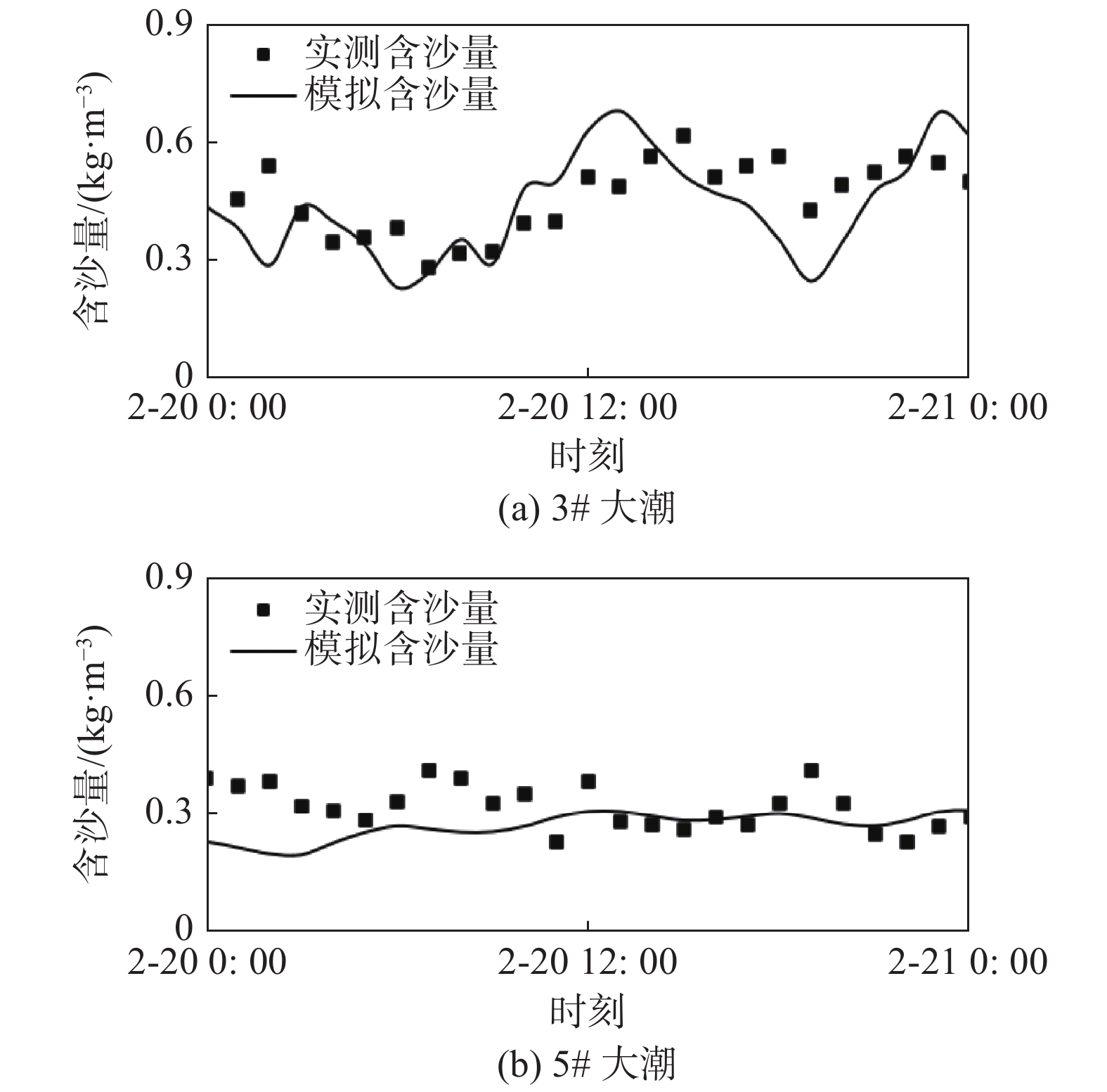
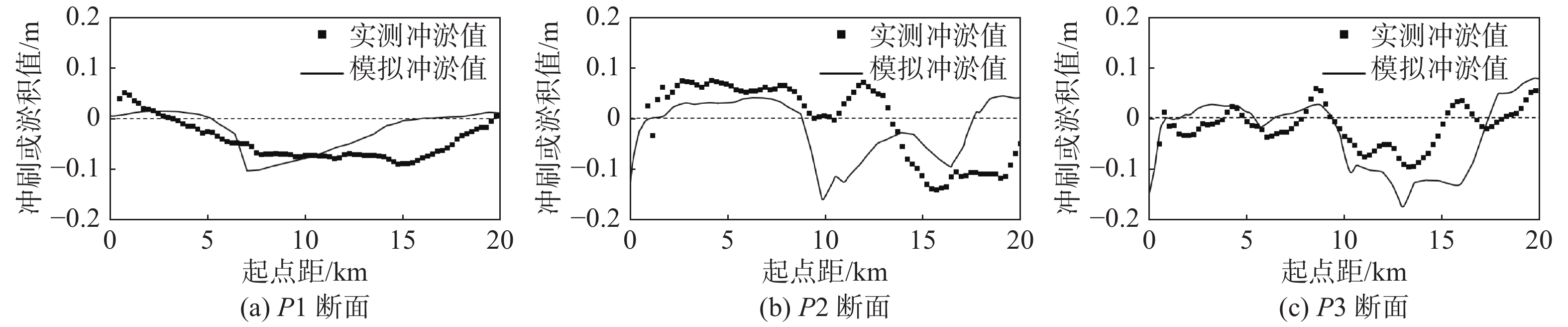
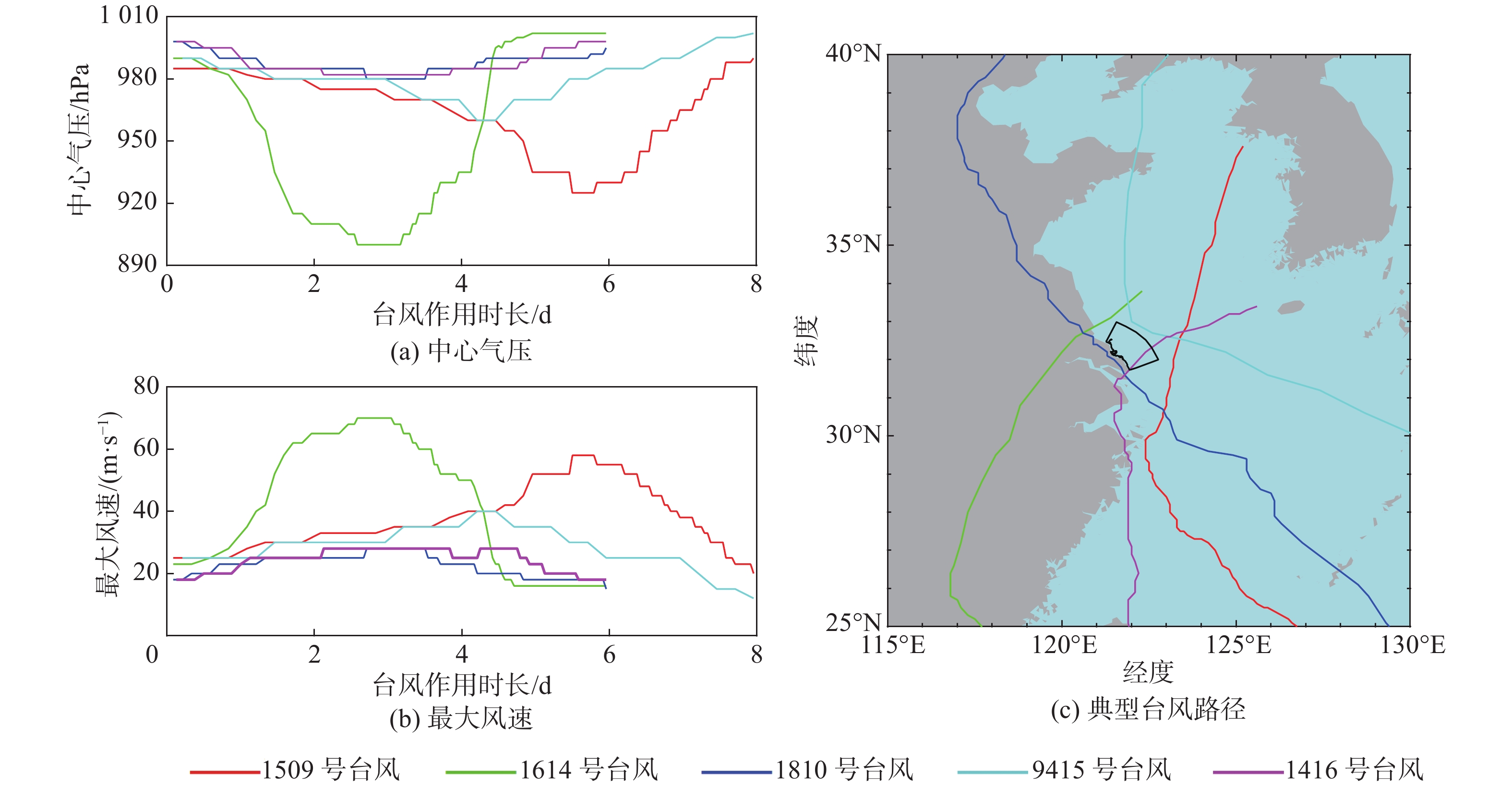
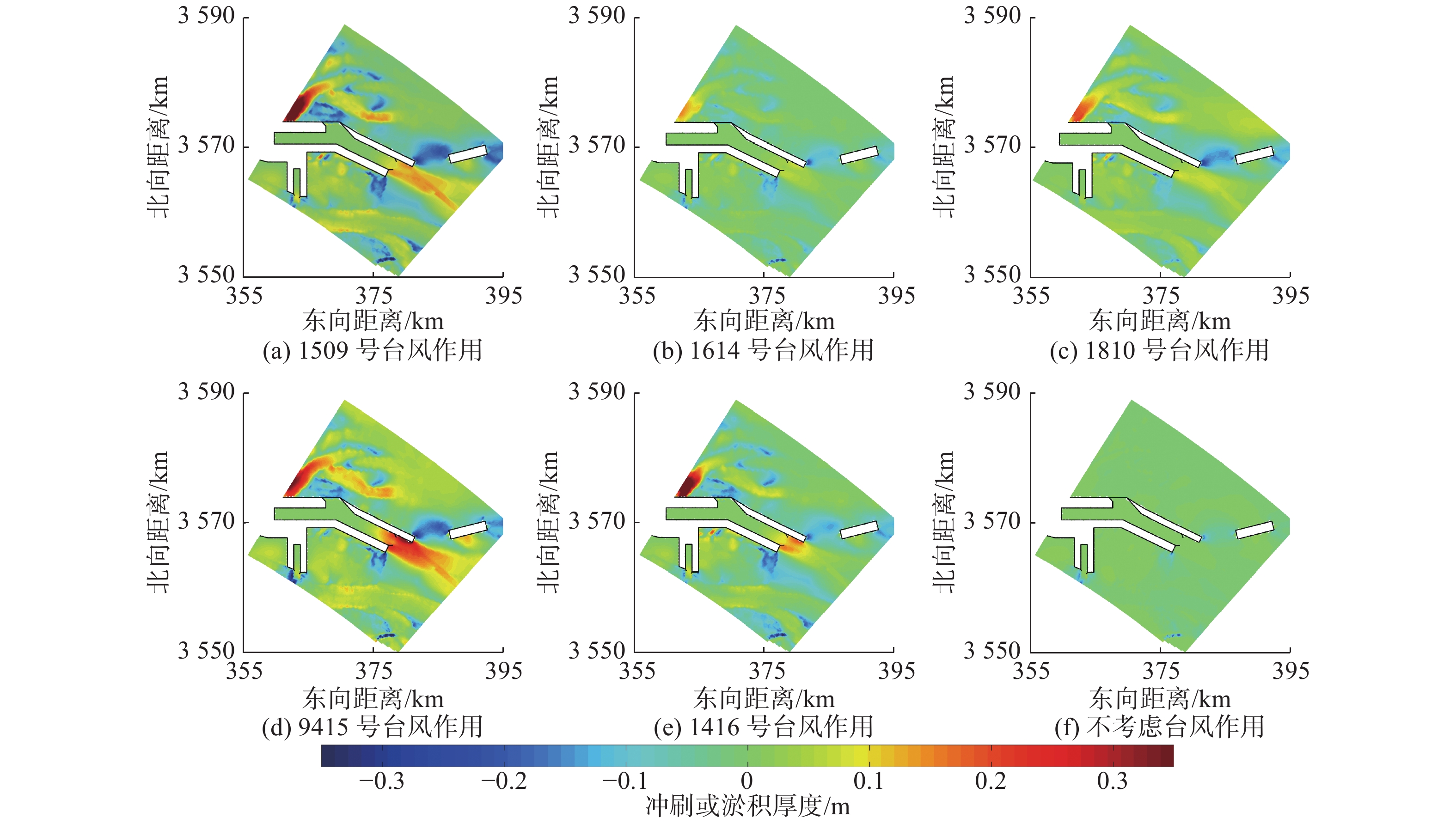
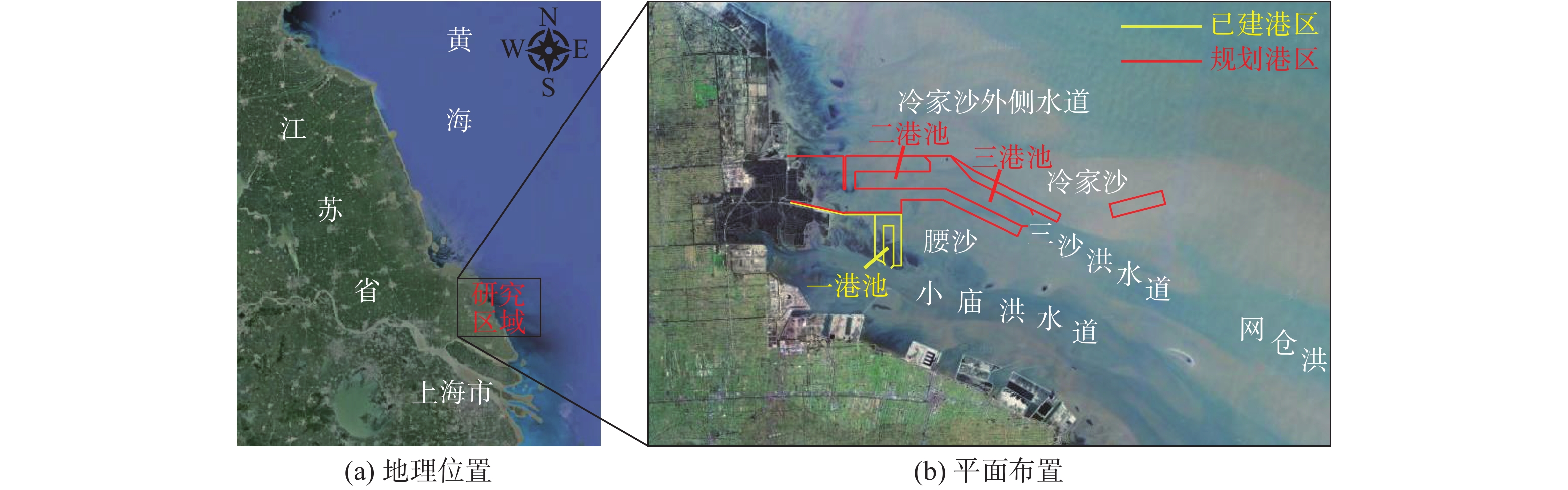
摘要: 基于ADCIRC+SWAN模式和Delft3D+SWAN模式建立双层嵌套的通州湾及周边海域的水沙动力数学模型。根据路径特征将影响通州湾的所有台风分为5类,选取每类的代表性台风驱动模型,模拟不同类型台风期间通州湾规划港区及周边水道沙洲系统的泥沙冲淤情况,剖析水道沙洲系统对台风暴潮的响应。结果表明:台风造成的通州湾规划港区及周边水道沙洲冲淤变化总体不大,在±0.40 m以内;北侧掠过型和东侧掠过型台风引起的海域冲淤相对较大;从空间分布上看,三港池口门附近及口外航道内容易淤积,腰沙、冷家沙浅滩区容易侵蚀。风暴期间港区北部冷家沙外侧水道出现严重淤积,原冷家沙浅滩区出现显著侵蚀,虽然一场风暴过程的冲淤量不足以影响港口运营及通航,但需注意长期时间尺度上对总体冲淤趋势的影响。Abstract: A nested morphodynamic model of the Tongzhou Bay and its surrounding sea areas is set up with ADCIRC+SWAN and Delft3D+SWAN models. All Typhoons that affected the Tongzhou Bay during 1949 to 2019 are classified into five types according to the characteristics of their tracks, and for each type a typical typhoon is selected to drive the model. The morphodynamic changes of the study area induced by the typical typhoons are simulated, and the responses of channel-sand system in Tongzhou Bay and its surrounding sea areas to storm surges are analyzed. The results show that the thickness of sediment erosion and deposition in the planning port area during a typical typhoon process is generally small, within about ±0.40 m. The erosion and sedimentation induced by the north-passing typhoon and the east-passing typhoon are relatively large. Generally, siltation usually occurs outside the entrance of the Basin 3 of the Tongzhou Bay port area, while erosion usually occurs in the Yaosha and Lengjiasha shoals. After a typhoon process, obvious siltation occurred in the outer channel of Lengjiasha in the north of the port area, and obvious erosion occurred in the original Lengjiasha shoal area. Although the amount of siltation/erosion induced by one storm process is not large enough to affect the port operation and navigation, attention should be paid to the impacts of such siltation/erosion in a long-term time scale.
-
Keywords:
- Tongzhou Bay /
- planning port area /
- storm surge /
- numerical simulation /
- erosion and siltation
-
-
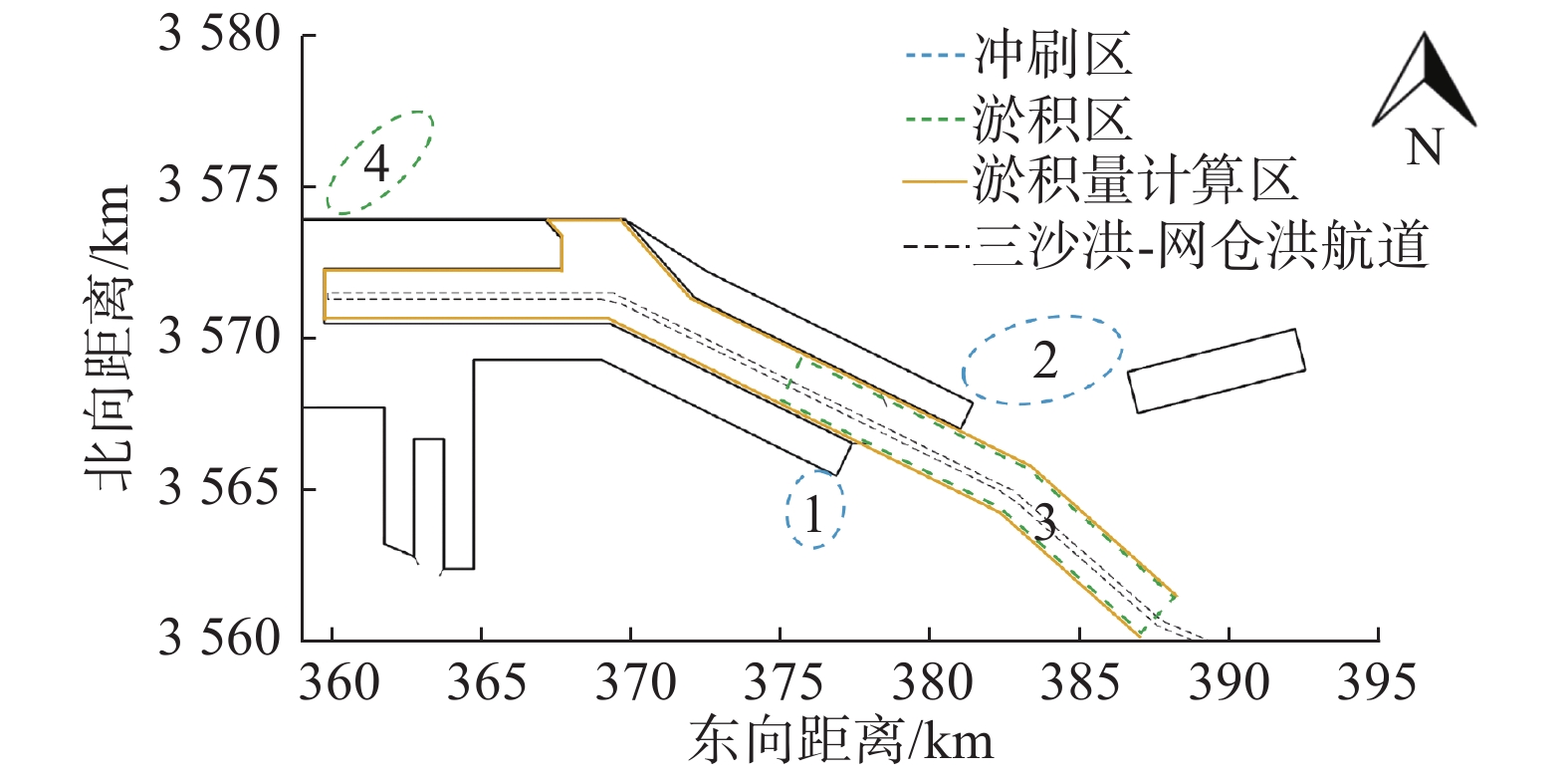
表 1 台风后选定区域内泥沙淤积量及局部最大冲淤幅度对比
Table 1 Comparison of the sedimentation volume and the maximum erosion and siltation range within the selected area after the typical typhoons
典型台风及类型 淤积总量/万m3 局部最大淤积厚度/m 局部最大冲刷厚度/m 1509号台风(东侧掠过型) 222.7 0.17 0.34 1614号台风(西侧掠过型) 51.9 0.08 0.27 1810号台风(南侧掠过型) 92.9 0.08 0.33 9415号台风(北侧掠过型) 347.3 0.35 0.39 1416号台风(直接穿过型) 126.4 0.19 0.23 -
[1] 俞亮亮, 陈可锋, 陆培东, 等. 海平面上升背景下辐射沙脊风暴潮增水研究[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2014(6):52-57. (YU Liangliang, CHEN Kefeng, LU Peidong, et al. A study of storm surge in radial sand ridges under sea level rising[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2014(6): 52-57. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-640X.2014.06.008 [2] 朴正, 吴永强. 通州湾北部港区起步工程选址研究[J]. 港工技术,2020,57(增刊1):17-21. (PIAO Zheng, WU Yongqiang. The study on site selection of initial project of Tongzhou Bay northern port area[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2020, 57(Suppl1): 17-21. (in Chinese) [3] 谢灵运, 王勇, 白玉川. 通州湾建港工程对辐射沙洲海域潮流泥沙条件的影响[J]. 港工技术,2016,53(4):1-6. (XIE Lingyun, WANG Yong, BAI Yuchuan. Impact of Tongzhou Gulf port project on tidal current and sediment conditions of radial shoal area[J]. Port Engineering Technology, 2016, 53(4): 1-6. (in Chinese) [4] 南京水利科学研究院. 南通港通州湾港区建港自然条件研究(专题一)——海岸稳定性与建港条件专题研究[R]. 南京: 南京水利科学研究院, 2011. Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute. Research on natural conditions of port building in Tongzhou Bay port area of Nantong Port(subject 1)—thematic study on coastal stability and port construction conditions[R]. Nanjing: Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, 2011. (in Chinese)
[5] 南京水利科学研究院. 南通港通州湾港区总体规划方案研究(专题一)——通州湾港区建港自然条件综合分析[R]. 南京: 南京水利科学研究院, 2013. Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute. Research on the master plan of Tongzhou Bay port area of Nantong Port(subject 1)—Comprehensive analysis of the natural conditions for port construction in Tongzhou Bay port area[R]. Nanjing: Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, 2013. (in Chinese)
[6] 陈可锋, 陆培东, 喻国华. 辐射沙脊小庙洪水道口门形态演变及其水动力机制研究[J]. 中山大学学报(自然科学版),2012,51(2):101-106. (CHEN Kefeng, LU Peidong, YU Guohua. Hydrodynamic mechanism of morphology revolution of the Xiaomiaohong tidal channel in radial sand ridges, Jiangsu Province[J]. Acta Scientiarum Naturalium Universitatis Sunyatseni, 2012, 51(2): 101-106. (in Chinese) [7] 南京水利科学研究院. 网仓洪航道开发自然条件研究[R]. 南京: 南京水利科学研究院, 2014. Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute. Research on natural conditions of Wangcanghong Channel development[R]. Nanjing: Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, 2014. (in Chinese)
[8] 王昌保, 王仙美, 翟剑峰, 等. 江苏南黄海辐射沙脊群建港条件及关键技术[M]. 南京: 河海大学出版社, 2015. WANG Changbao, WANG Xianmei, ZHAI Jianfeng, et al. Port construction conditions and key technologies of radiation sand ridges in the southern Yellow Sea, Jiangsu[M]. Nanjing: Hohai University Press, 2015. (in Chinese)
[9] 纪为刚, 付桂. 南通通州湾港区水文泥沙特性分析[J]. 中国水运,2015,15(8):204-208. (JI Weigang, FU Gui. Analysis of hydrological and sediment characteristics in Tongzhou Bay port area of Nantong[J]. China Water Transport, 2015, 15(8): 204-208. (in Chinese) [10] 陆培东. 江苏省如东县人工岛工程泥沙物理模型试验研究[R]. 南京: 南京水利科学研究院, 2003. LU Peidong. Experimental study on sediment physical model of artificial island project in Rudong County, Jiangsu Province[R]. Nanjing: Nanjing Hydraulic Research Institute, 2003. (in Chinese)
[11] DIETRICH J C, ZIJLEMA M, WESTERINK J J, et al. Modeling hurricane waves and storm surge using integrally-coupled, scalable computations[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2011, 58(1): 45-65. doi: 10.1016/j.coastaleng.2010.08.001
[12] CHEN Q, WANG H Q, WANG L X, et al. Predicting the impacts of tropical cyclones and sea-level rise on beach mouse habitat[J]. Journal of Coastal Research, 2014, 68(Suppl1): 12-19.
[13] WL|Delft Hydraulics. Delft3D-WAVE: Simulation of short-crested waves with SWAN—user manual[M]. Delft: Deltares, 2018.
[14] 杨万康, 尹宝树, 伊小飞, 等. 基于Holland风场的台风浪数值计算[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2017(4):28-34. (YANG Wankang, YIN Baoshu, YI Xiaofei, et al. Numerical calculation and research of typhoon waves based on Holland wind field[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2017(4): 28-34. (in Chinese) [15] 王仙美, 翟剑峰, 东培华, 等. 基于台风参数模型的江苏海域风暴增减水研究[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2015(2):61-66. (WANG Xianmei, ZHAI Jianfeng, DONG Peihua, et al. A study of storm surge in Jiangsu sea waters based on a typhoon parameter model[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2015(2): 61-66. (in Chinese) [16] ALLEN J J, SOMERFIELD P J, GILBERT F J. Quantifying uncertainty in high-resolution coupled hydrodynamic-ecosystem models[J]. Journal of Marine Systems, 2007, 64(1/4): 3-14.


 Email Alerts
Email Alerts RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: