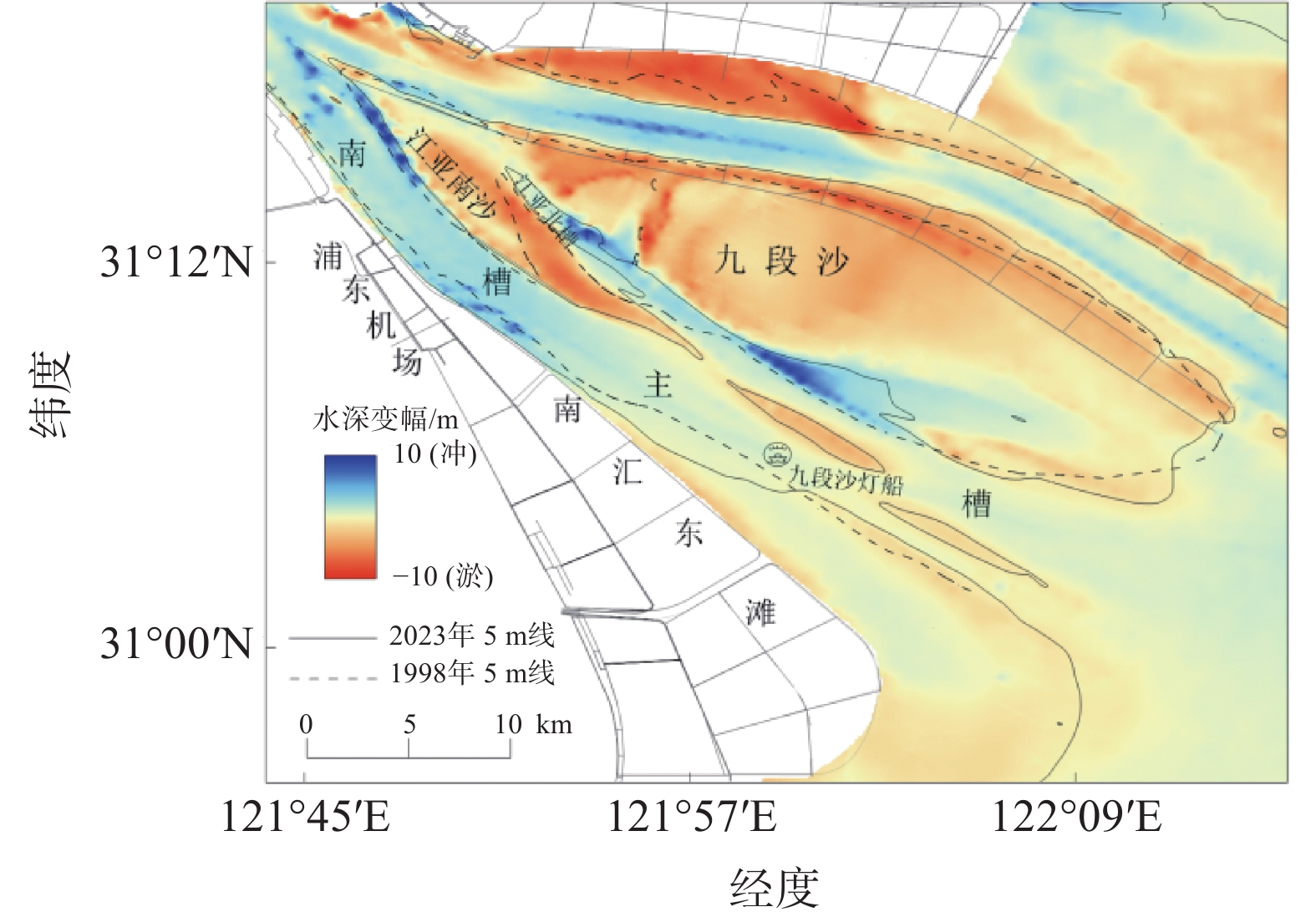
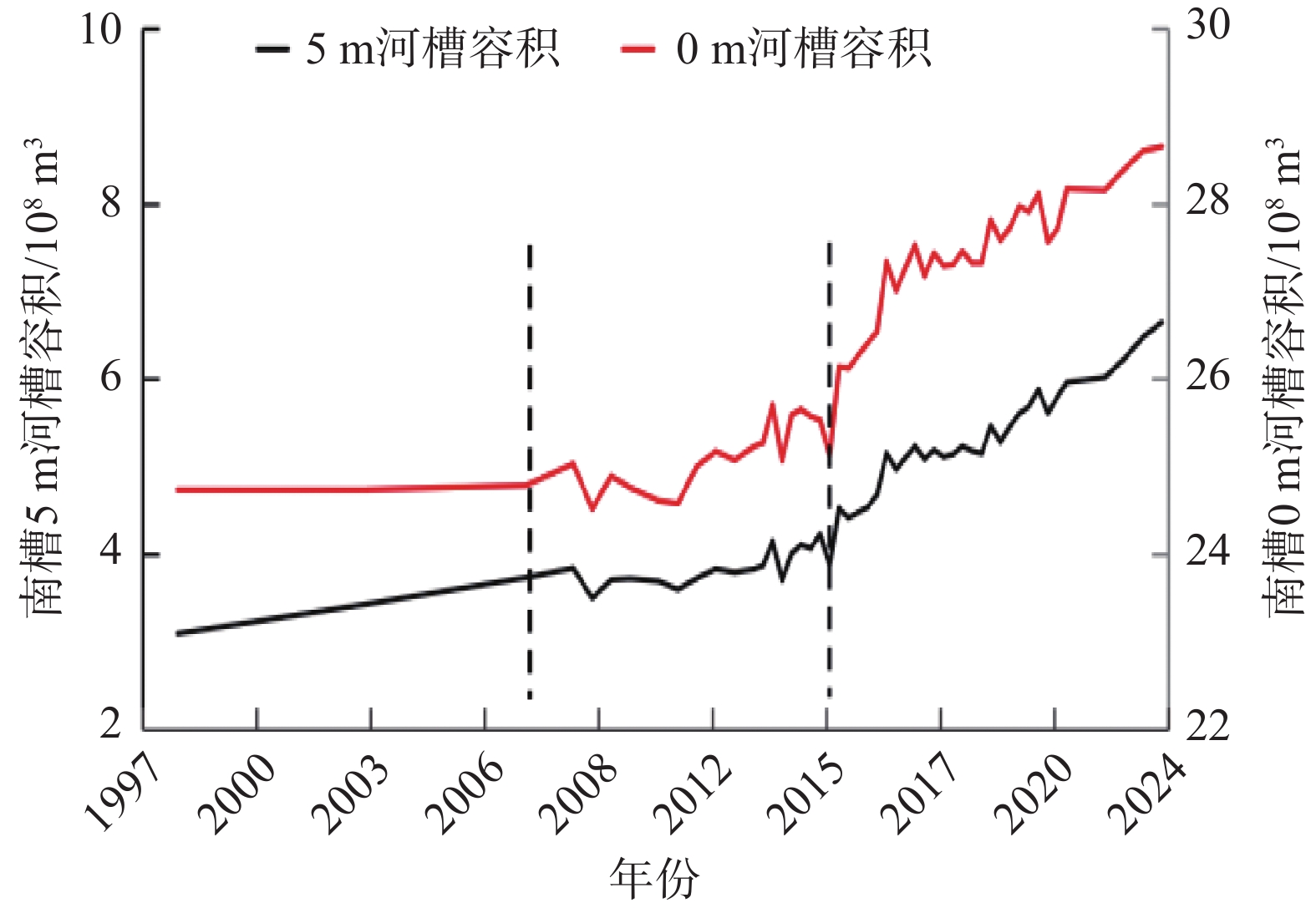
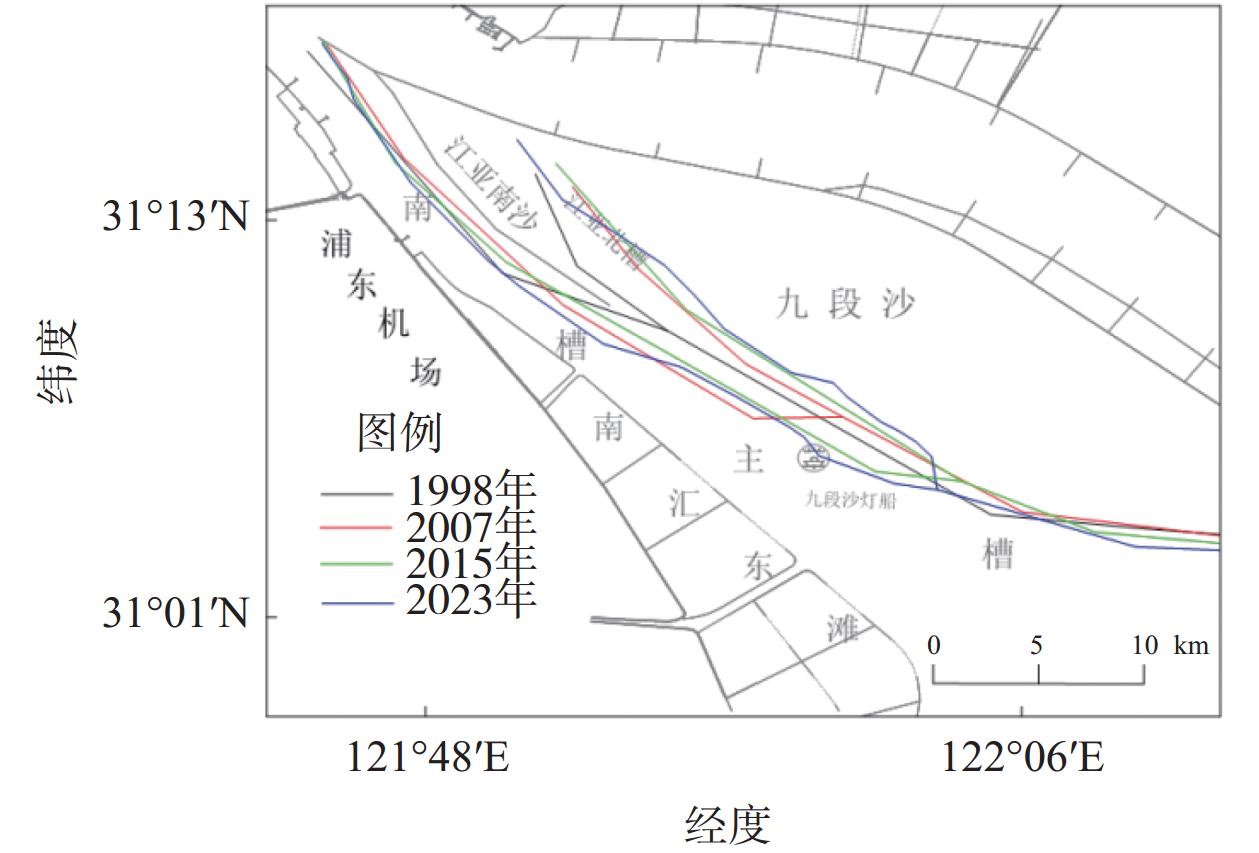
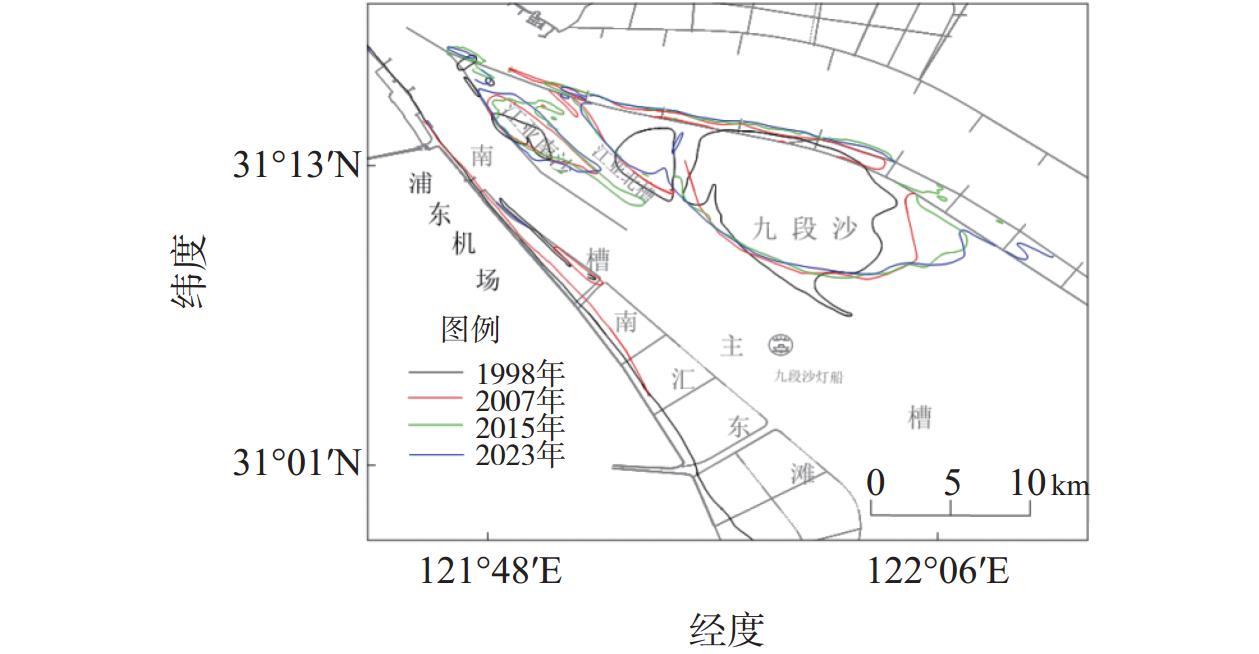
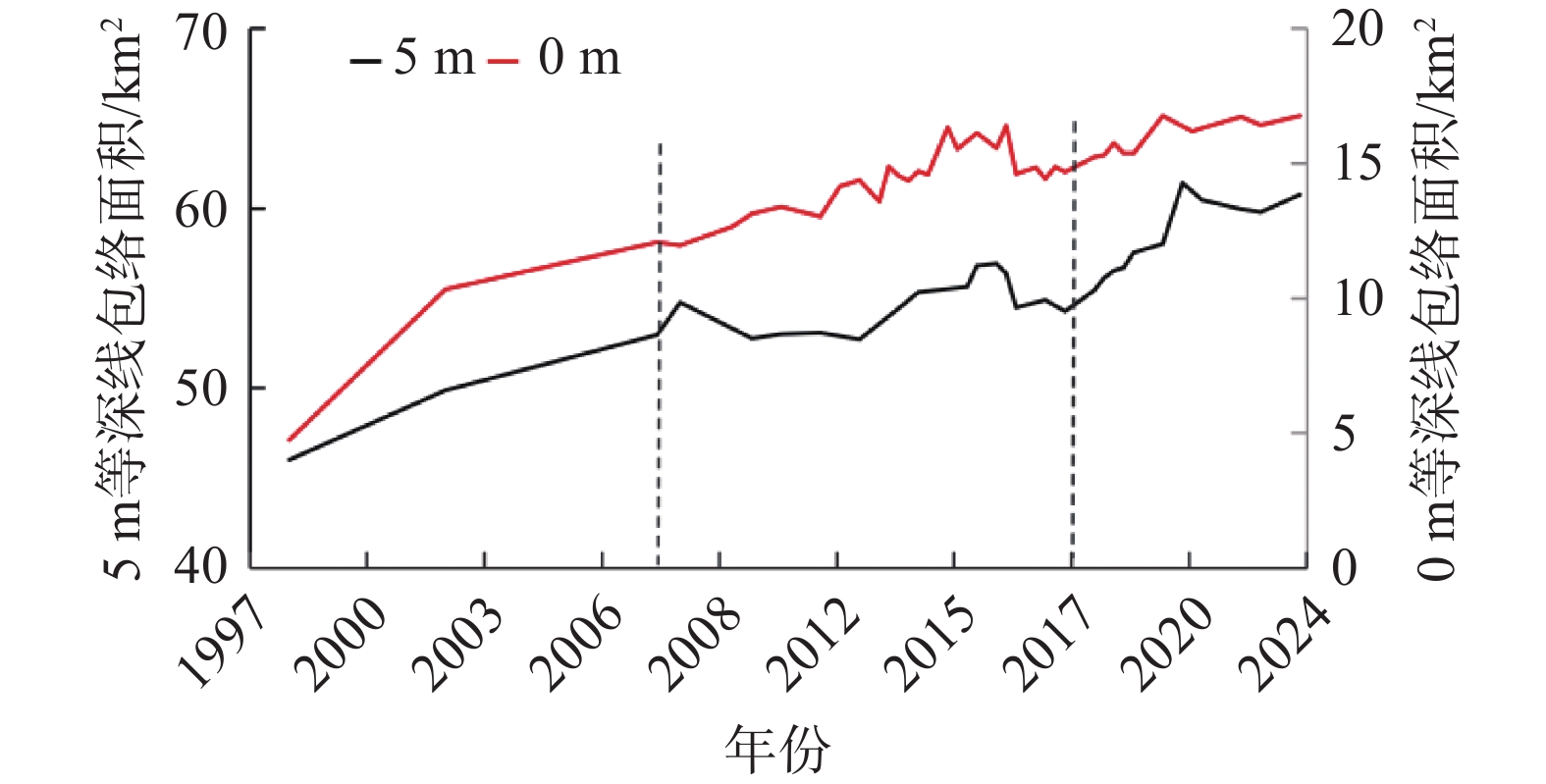
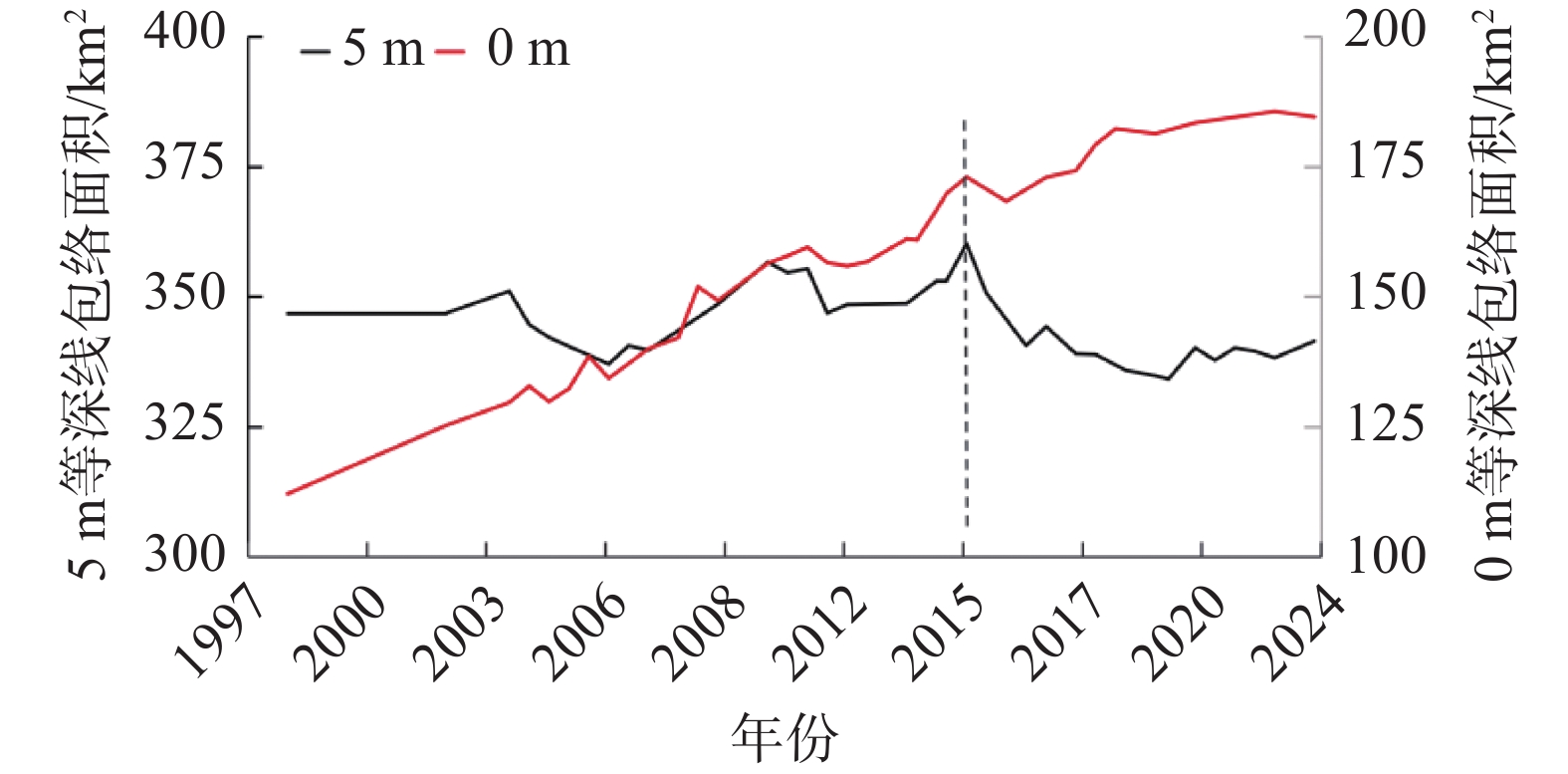
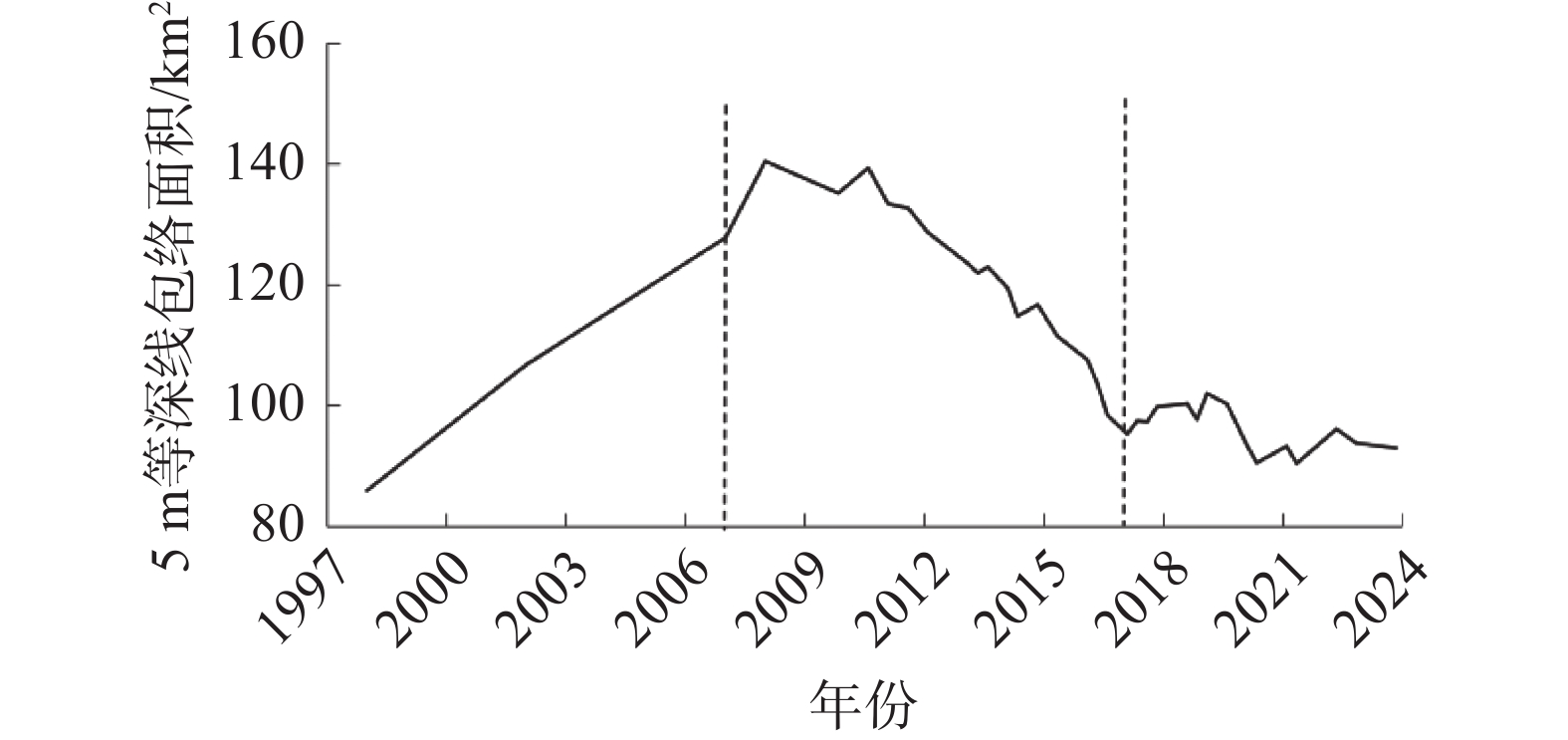
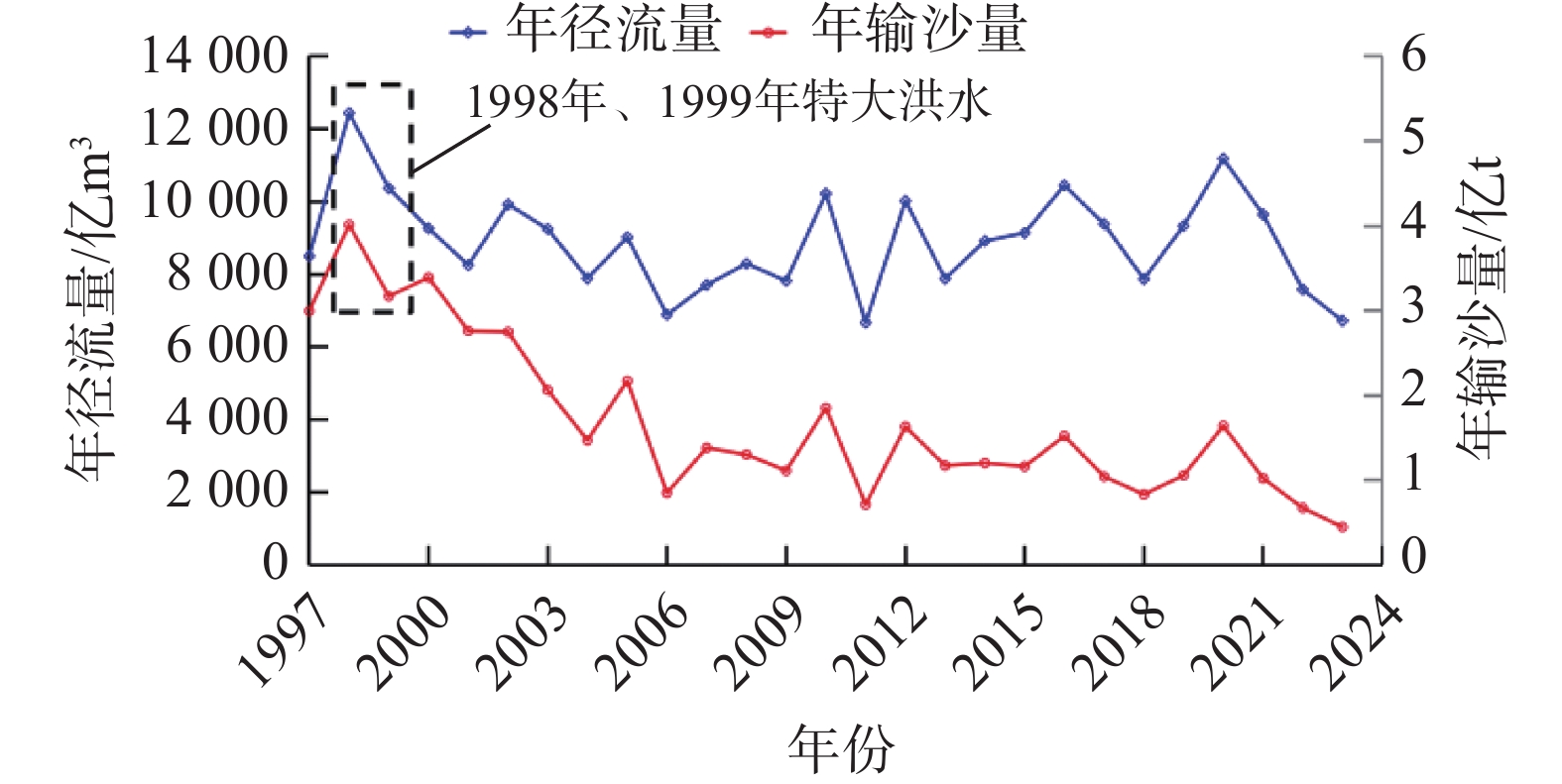
Bed evolution characteristics and influencing factors of the South Passage of the Yangtze Estuary (1998–2023)
-
摘要:
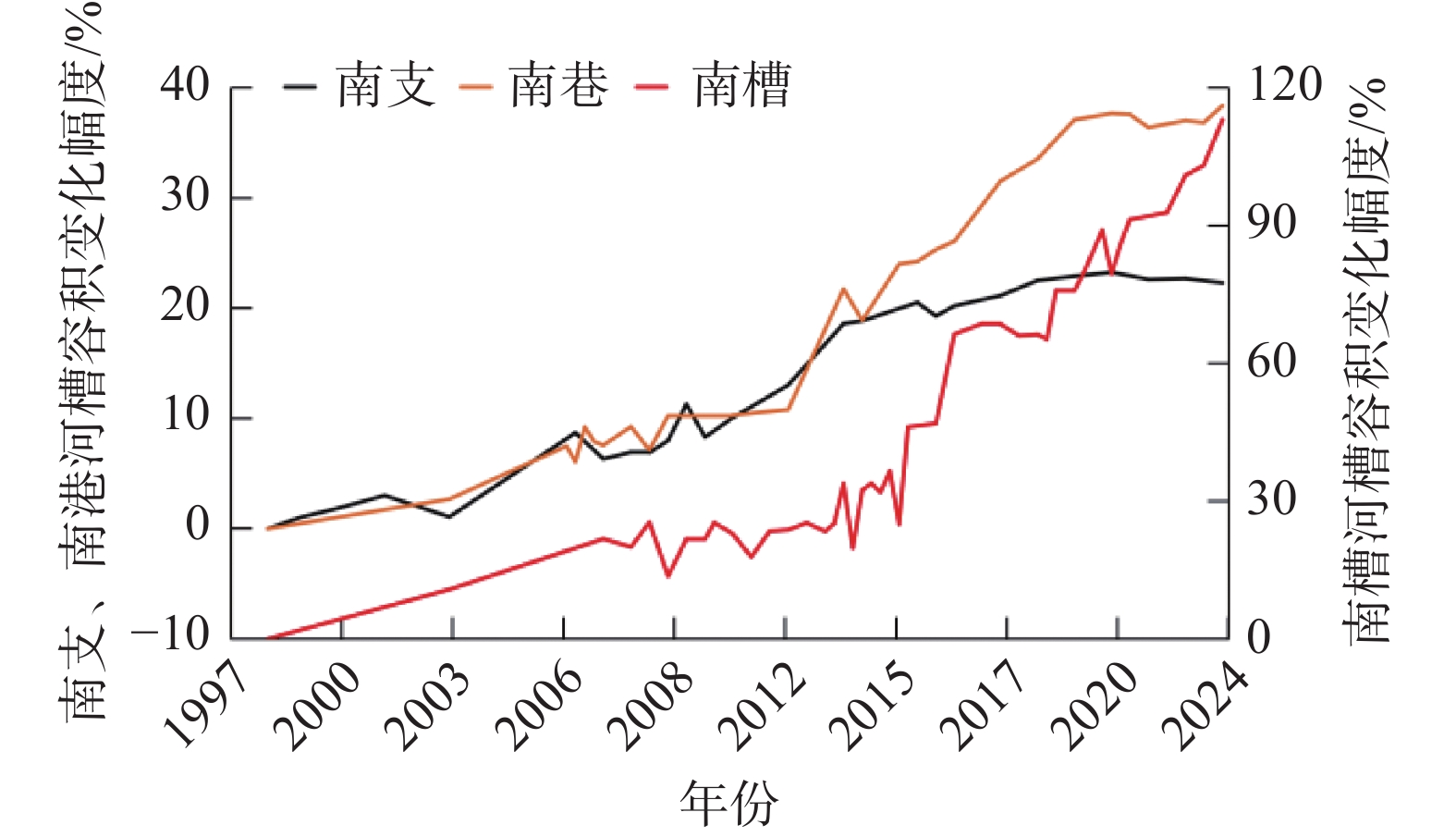
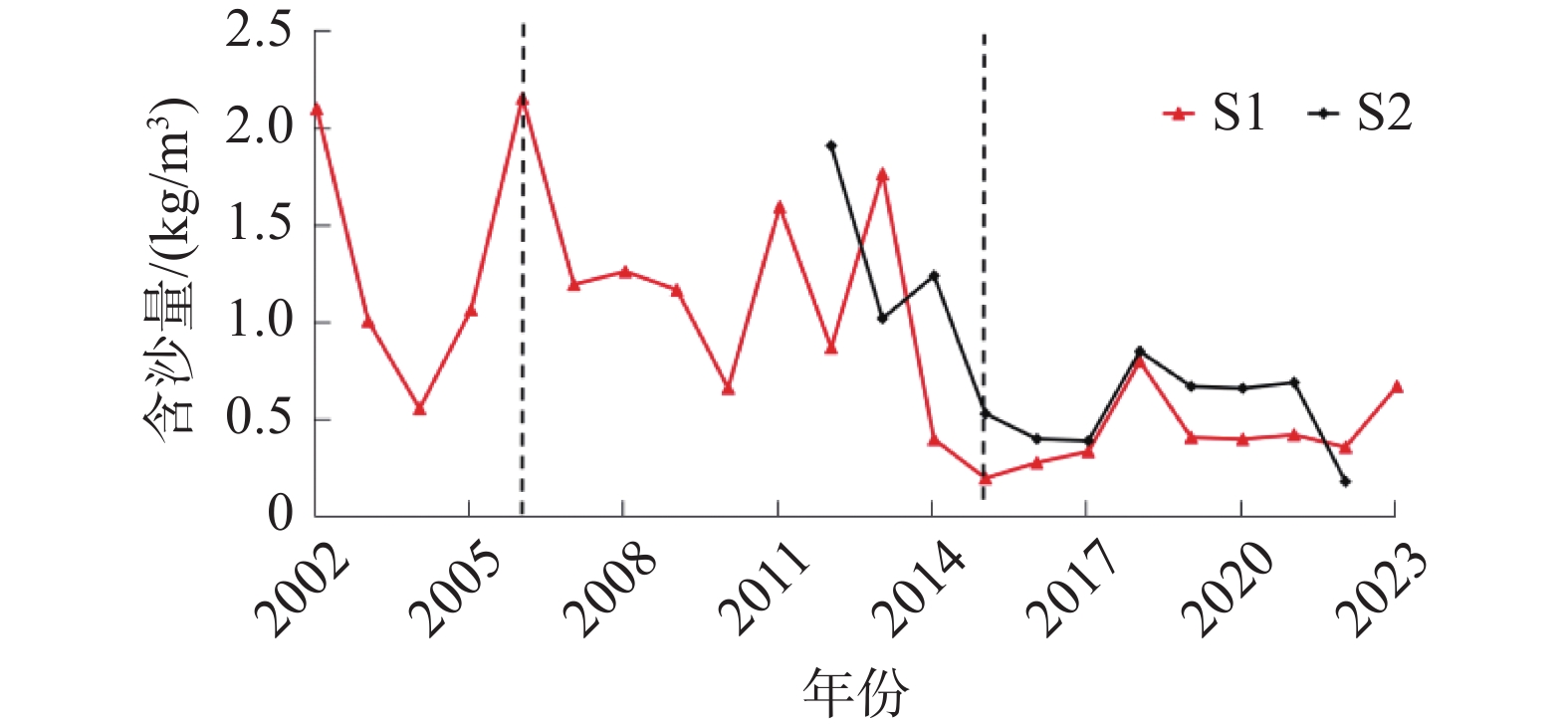
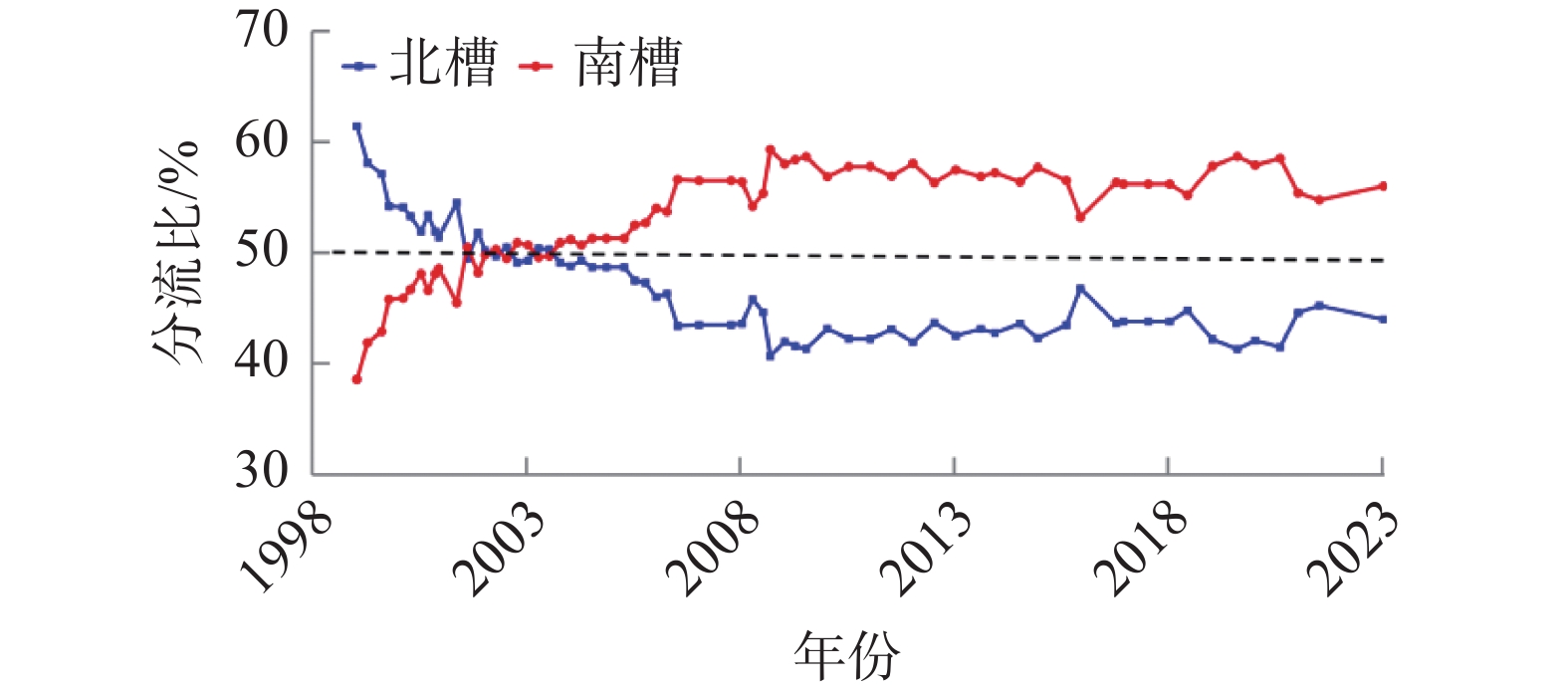
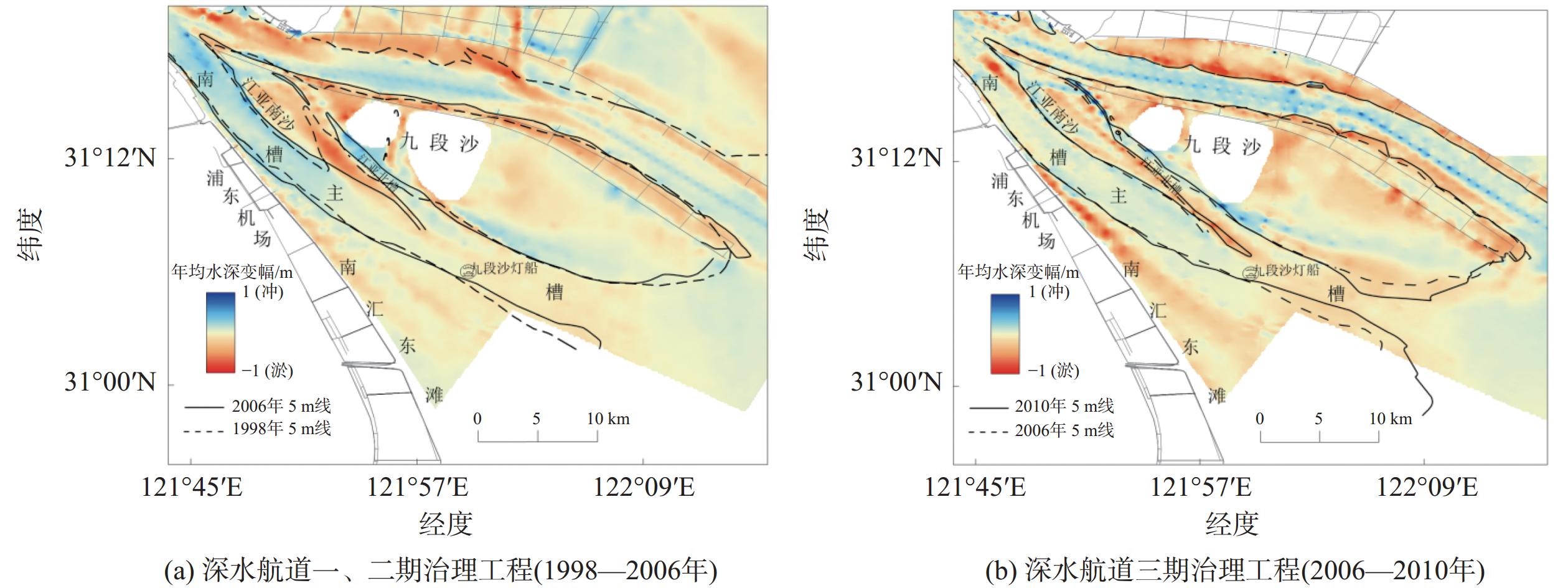
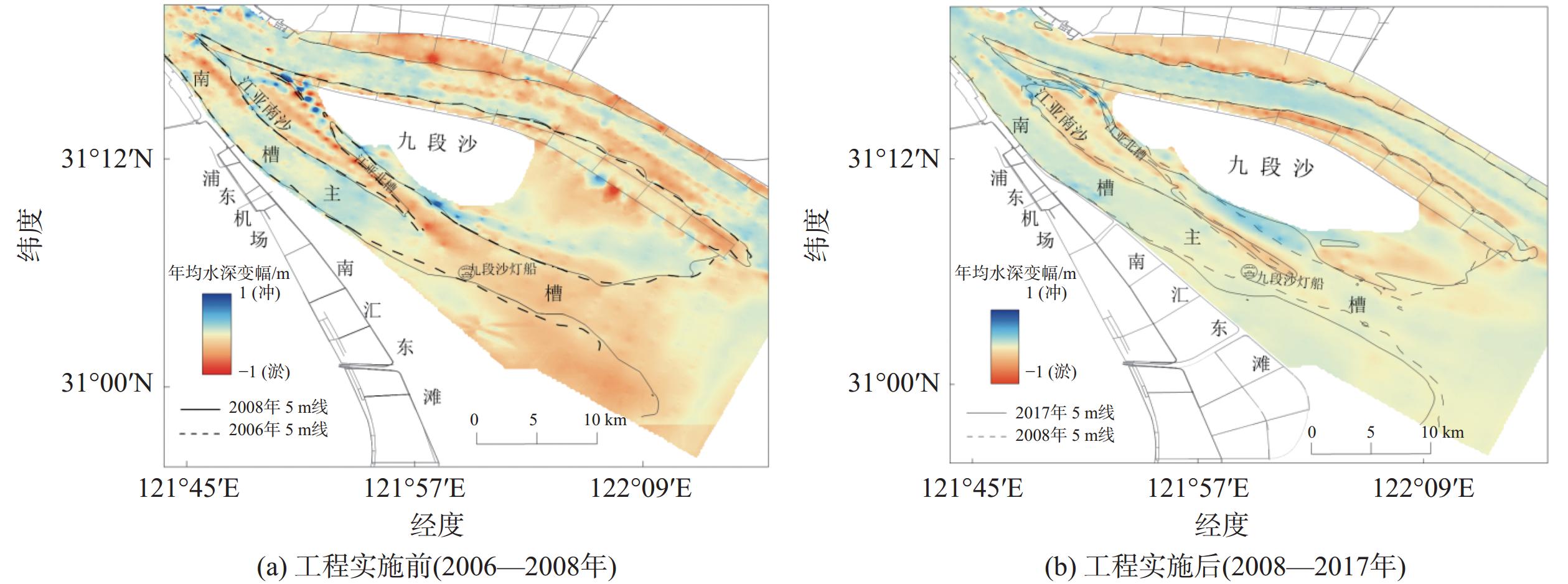
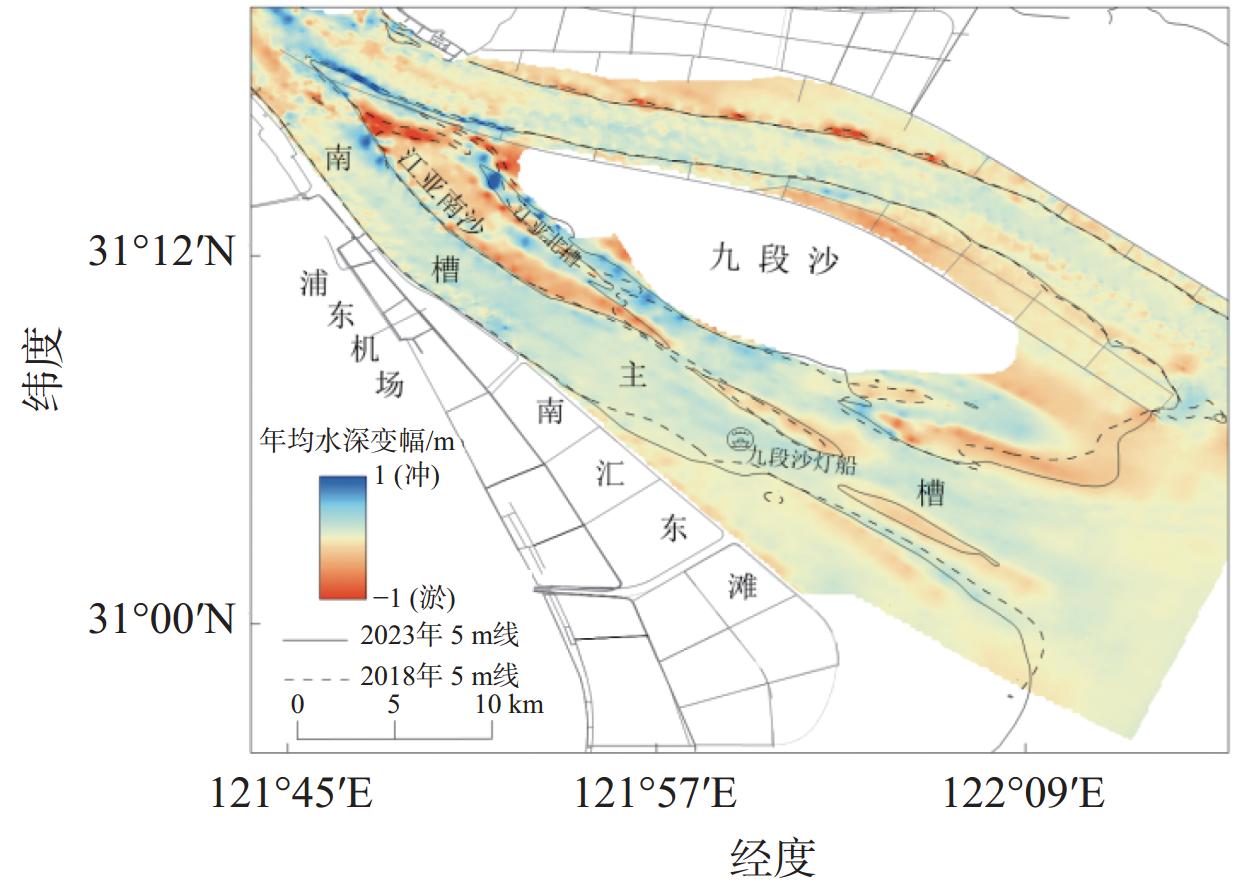
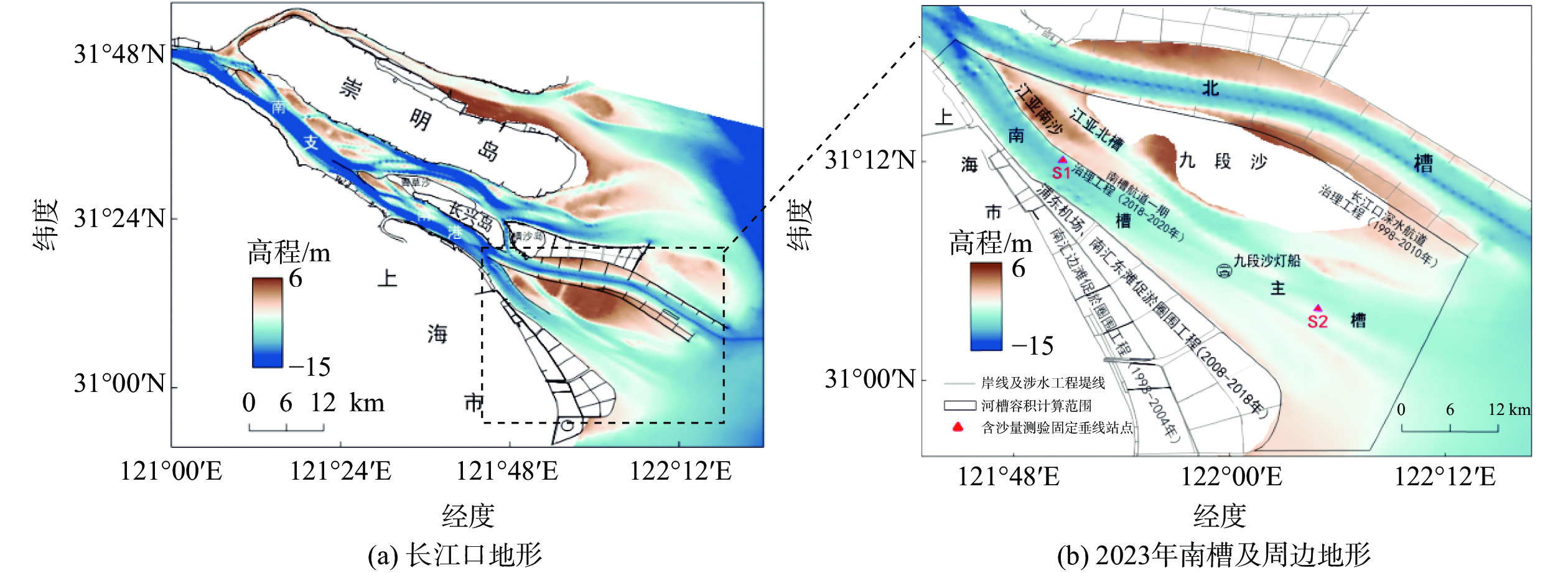
南槽作为长江口的入海汊道之一,其河床演变动态受到广泛关注。基于长江口南槽1998年以来长序列水下地形、水沙观测数据和大型涉水工程实施情况,分析南槽近期河床冲淤变化过程,从流域减沙和工程建设两方面探讨河床演变特征及影响过程。结果表明:近25年,南槽河床演变总体呈现“缓慢冲刷-趋于平衡-加速冲刷”的三阶段变化特征,其中第一阶段的“缓慢冲刷”主要受工程建设影响,流域减沙则是第三阶段“加速冲刷”的主要因素之一。未来,在稳定河床边界和较低含沙量条件下,南槽短期内仍将延续冲刷态势,直至趋于新的平衡。
Abstract:As a inlet of the Yangtze Estuary, the bed evolution dynamics of the South Passage have attracted widespread attention. Based on long-term underwater topographic and sediment data, along with large-scale water-related engineering implementation since 1998, this study analyzes the recent bed erosion and deposition processes of the South Passage. The characteristics and influencing processes of bed evolution are discussed from two aspects: watershed sediment reduction and engineering construction. The results indicate that over the past 25 years, the bed evolution of the South Passage has shown a three-stage change pattern: "slow erosion–approaching equilibrium–accelerated erosion." The first stage of "slow erosion" was primarily influenced by engineering construction, while watershed sediment reduction is one of the main factors driving the "accelerated erosion" in the third stage. In the future, under conditions of a stabilized riverbed boundary and lower sediment concentration, the South Passage is likely to continue the erosion trend in the short term until a new equilibrium is reached.
-
Keywords:
- South Passage /
- bed evolution /
- sediment dynamics /
- water-related engineering
-
-
[1] PERILLO G M E, PÉREZ D E, PICCOLO M C, et al. Geomorphologic and physical characteristics of a human impacted estuary: Quequén Grande River Estuary, Argentina[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2005, 62(1/2): 301-312.
[2] TRAINI C, PROUST J N, MENIER D, et al. Distinguishing natural evolution and human impact on estuarine morpho-sedimentary development: a case study from the Vilaine Estuary, France[J]. Estuarine, Coastal and Shelf Science, 2015, 163: 143-155. doi: 10.1016/j.ecss.2015.06.025
[3] WANG Y H, XU C L, DONG P, et al. Impact of human intervention on channel shrinkage and restoration in the Huanghe Estuary[J]. Environmental Earth Sciences, 2020, 79(10): 238. doi: 10.1007/s12665-020-08988-3
[4] 王俊, 田淳, 张志林. 长江口河道演变规律与治理研究[M]. 北京: 中国水利水电出版社, 2013. (WANG Jun, TIAN Chun, ZHANG Zhilin. Study on the evolution law and regulation of the Yangtze River Estuary[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2013. (in Chinese) WANG Jun, TIAN Chun, ZHANG Zhilin. Study on the evolution law and regulation of the Yangtze River Estuary[M]. Beijing: China Water & Power Press, 2013. (in Chinese)
[5] 黄宇明, 缴健, 窦希萍, 等. 基于Copula函数的大通站水沙特征分析[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2022(4):37-45. (HUANG Yuming, JIAO Jian, DOU Xiping, et al. Analysis of runoff and sediment characteristics of Datong Station based on Copula function[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2022(4): 37-45. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20210408003 HUANG Yuming, JIAO Jian, DOU Xiping, et al. Analysis of runoff and sediment characteristics of Datong Station based on Copula function[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2022(4): 37-45. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20210408003
[6] 万远扬, 吴华林. 径流量变化对长江口北槽最大浑浊带影响分析[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2021(5):1-7. (WAN Yuanyang, WU Hualin. Study on the effect of river inflow on estuarine turbidity maximum in the North Passage of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2021(5): 1-7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20210422001 WAN Yuanyang, WU Hualin. Study on the effect of river inflow on estuarine turbidity maximum in the North Passage of the Yangtze Estuary[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2021(5): 1-7. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20210422001
[7] 刘杰, 程海峰, 韩露, 等. 流域水沙变化和人类活动对长江口河槽演变的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2021(2):1-9. (LIU Jie, CHENG Haifeng, HAN Lu, et al. New trends of river channel evolution of the Yangtze River estuary under the influences of inflow and sediment variations and human activities[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2021(2): 1-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20200313001 LIU Jie, CHENG Haifeng, HAN Lu, et al. New trends of river channel evolution of the Yangtze River estuary under the influences of inflow and sediment variations and human activities[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2021(2): 1-9. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20200313001
[8] 赵庆英, 杨世伦, 朱骏. 河口河槽季节性冲淤变化及其对河流来水来沙响应的统计分析: 以长江口南槽为例[J]. 地理科学,2003,23(1):112-117. (ZHAO Qingying, YANG Shilun, ZHU Jun. The statistical analysis of response of the river mouth passage to water and sediment discharges from the Changjiang River[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 23(1): 112-117. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.01.020 ZHAO Qingying, YANG Shilun, ZHU Jun. The statistical analysis of response of the river mouth passage to water and sediment discharges from the Changjiang River[J]. Scientia Geographica Sinica, 2003, 23(1): 112-117. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-0690.2003.01.020
[9] 杨世伦, 朱骏, 赵庆英. 长江供沙量减少对水下三角洲发育影响的初步研究: 近期证据分析和未来趋势估计[J]. 海洋学报,2003,25(5):83-91. (YANG Shilun, ZHU Jun, ZHAO Qingying. A preliminary study on the influence of Changjiang River sediment supply on subaqueous delta: Evidences in late 20th century and an expectation for the coming decades[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2003, 25(5): 83-91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2003.05.010 YANG Shilun, ZHU Jun, ZHAO Qingying. A preliminary study on the influence of Changjiang River sediment supply on subaqueous delta: Evidences in late 20th century and an expectation for the coming decades[J]. Acta Oceanologica Sinica, 2003, 25(5): 83-91. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:0253-4193.2003.05.010
[10] 谢华亮. 长江口南槽近期动力地貌演变研究[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2014. (XIE Hualiang. The recent morphodynamic evolution of the south passage, Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2014. (in Chinese) XIE Hualiang. The recent morphodynamic evolution of the south passage, Changjiang (Yangtze) Estuary[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2014. (in Chinese)
[11] 刘杰, 程海峰, 韩露, 等. 流域减沙对长江口典型河槽及邻近海域演变的影响[J]. 水科学进展,2017,28(2):249-256. (LIU Jie, CHENG Haifeng, HAN Lu, et al. Influence of fluvial sediment decline on the morphdynamics of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent seas[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2017, 28(2): 249-256. (in Chinese) LIU Jie, CHENG Haifeng, HAN Lu, et al. Influence of fluvial sediment decline on the morphdynamics of the Yangtze River Estuary and adjacent seas[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2017, 28(2): 249-256. (in Chinese)
[12] 杜景龙, 杨世伦, 张文祥, 等. 长江口北槽深水航道工程对九段沙冲淤影响研究[J]. 海洋工程,2005,23(3):78-83. (DU Jinglong, YANG Shilun, ZHANG Wenxiang, et al. Study of influence on erosion and accumulation of Jiuduansha tidal island by deep-water channel project at North passage of the Yangtze River[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2005, 23(3): 78-83. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2005.03.013 DU Jinglong, YANG Shilun, ZHANG Wenxiang, et al. Study of influence on erosion and accumulation of Jiuduansha tidal island by deep-water channel project at North passage of the Yangtze River[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2005, 23(3): 78-83. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2005.03.013
[13] 付桂, 李九发, 应铭, 等. 长江河口南汇嘴潮滩近期演变分析[J]. 海洋通报,2007,26(2):105-112. (FU Gui, LI Jiufa, YING Ming, et al. Analysis on recent topography evolution of Nanhuizui tidal flat in Yangtze Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2007, 26(2): 105-112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.02.016 FU Gui, LI Jiufa, YING Ming, et al. Analysis on recent topography evolution of Nanhuizui tidal flat in Yangtze Estuary[J]. Marine Science Bulletin, 2007, 26(2): 105-112. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6392.2007.02.016
[14] DAI Z J, LIU J T, WEI W, et al. Detection of the Three Gorges Dam influence on the Changjiang (Yangtze River) submerged delta[J]. Scientific Reports, 2014, 4: 6600. doi: 10.1038/srep06600
[15] 刘红, 应铭, 张华, 等. 工程条件下长江口南槽自适应过程[C]∥第十五届中国海洋(岸)工程学术讨论会论文集(中). 太原: 中国海洋工程学会, 2011: 518-525. (LIU Hong, YING Ming, ZHANG Hua, et al. The adaptive process of the South channel of the Yangtze Estuary under engineering conditions[C]∥Proceedings of the 15th China Ocean (Bank) Engineering Symposium (middle volume). Taiyuan: China Marine Engineering Society, 2011: 518-525. (in Chinese) LIU Hong, YING Ming, ZHANG Hua, et al. The adaptive process of the South channel of the Yangtze Estuary under engineering conditions[C]∥Proceedings of the 15th China Ocean (Bank) Engineering Symposium (middle volume). Taiyuan: China Marine Engineering Society, 2011: 518-525. (in Chinese)
[16] 戴志军, 韩震, 恽才兴. 长江口南槽沉积物特征和运移趋势[J]. 海洋湖沼通报,2005(2):72-78. (DAI Zhijun, HAN Zhen, YUN Caixing. Grainsize characteristics and transport trends of the sediment in the south channel of the Yangtze River[J]. Transaction of Oceanology and Limnology, 2005(2): 72-78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2005.02.013 DAI Zhijun, HAN Zhen, YUN Caixing. Grainsize characteristics and transport trends of the sediment in the south channel of the Yangtze River[J]. Transaction of Oceanology and Limnology, 2005(2): 72-78. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6482.2005.02.013
[17] 杨世伦, 丁平兴, 赵庆英. 开敞大河口滩槽冲淤对台风的响应及其动力泥沙机制探讨: 以长江口南汇边滩-南槽-九段沙系统为例[J]. 海洋工程,2002,20(3):69-75. (YANG Shilun, DING Pingxing, ZHAO Qingying. Morphodynamic response of a large river mouth to typhoons[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2002, 20(3): 69-75. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2002.03.012 YANG Shilun, DING Pingxing, ZHAO Qingying. Morphodynamic response of a large river mouth to typhoons[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2002, 20(3): 69-75. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-9865.2002.03.012
[18] 王浩斌. 风暴对长江口悬沙浓度的影响及其动力机制[D]. 上海: 华东师范大学, 2018. (WANG Haobin. A study of the suspended sediment concentration in response to the typhoon in the Yangtze Estuary and its dynamic mechanism[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2018. (in Chinese) WANG Haobin. A study of the suspended sediment concentration in response to the typhoon in the Yangtze Estuary and its dynamic mechanism[D]. Shanghai: East China Normal University, 2018. (in Chinese)
[19] 杨世伦, 贺松林, 谢文辉. 长江口九段沙的形成演变及其与南北槽发育的关系[J]. 海洋工程,1998,16(4):55-65. (YANG Shilun, HE Songlin, XIE Wenhui. The formation and evolution of the Jiuduansha tidal island as well as their relation to the development of the North and South passages in the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 1998, 16(4): 55-65. (in Chinese) YANG Shilun, HE Songlin, XIE Wenhui. The formation and evolution of the Jiuduansha tidal island as well as their relation to the development of the North and South passages in the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 1998, 16(4): 55-65. (in Chinese)
[20] 戴志军, 陈吉余, 程和琴, 等. 南汇边滩的沉积特征和沉积物输运趋势[J]. 长江流域资源与环境,2005,14(6):735-739. (DAI Zhijun, CHEN Jiyu, CHENG Heqin, et al. Sediment characteristics and transport patterns in Nanhui joint area[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2005, 14(6): 735-739. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2005.06.013 DAI Zhijun, CHEN Jiyu, CHENG Heqin, et al. Sediment characteristics and transport patterns in Nanhui joint area[J]. Resources and Environment in the Yangtze Basin, 2005, 14(6): 735-739. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-8227.2005.06.013
[21] ZHU C Y, GUO L C, VAN MAREN D S, et al. Decadal morphological evolution of the mouth zone of the Yangtze Estuary in response to human interventions[J]. Earth Surface Processes and Landforms, 2019, 44(12): 2319-2332. doi: 10.1002/esp.4647
[22] 程海峰, 辛沛, 刘杰, 等. 1959—2018年九段沙地貌演化特征及动力机制[J]. 水科学进展,2020,31(4):491-501. (CHENG Haifeng, XIN Pei, LIU Jie, et al. Morphological evolution and dynamic mechanics of the Jiuduansha Shoal (China) during 1959-2018[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2020, 31(4): 491-501. (in Chinese) CHENG Haifeng, XIN Pei, LIU Jie, et al. Morphological evolution and dynamic mechanics of the Jiuduansha Shoal (China) during 1959-2018[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2020, 31(4): 491-501. (in Chinese)
[23] 王芬, 谭亚, 刘士诚. 海平面上升对长江江阴以下河段风暴潮增水的影响[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2023(1):43-52. (WANG Fen, TAN Ya, LIU Shicheng. Influence of sea level rise on storm surge water increase in the reach below Jiangyin of the Yangtze River[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2023(1): 43-52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20220228002 WANG Fen, TAN Ya, LIU Shicheng. Influence of sea level rise on storm surge water increase in the reach below Jiangyin of the Yangtze River[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2023(1): 43-52. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12170/20220228002
[24] 上海河口海岸科学研究中心. 长江口典型滩槽冲淤演变特征及对周围环境影响分析报告[R]. 上海: 上海河口海岸科学研究中心, 2019. (Shanghai Estuarine and Shanghai Estuarine and Coastal Science Research Center. The evolution characteristics of the Yangtze Estuary and its impact on the surrounding environment[R]. Shanghai: Shanghai Estuarine and Shanghai Estuarine and Coastal Science Research Center, 2019. (in Chinese) Shanghai Estuarine and Shanghai Estuarine and Coastal Science Research Center. The evolution characteristics of the Yangtze Estuary and its impact on the surrounding environment[R]. Shanghai: Shanghai Estuarine and Shanghai Estuarine and Coastal Science Research Center, 2019. (in Chinese)
[25] 刘杰, 陈吉余, 徐志扬. 长江口深水航道治理工程实施后南北槽分汊段河床演变[J]. 水科学进展,2008,19(5):605-612. (LIU Jie, CHEN Jiyu, XU Zhiyang. River-bed evolution in the braided reach of the south and north passage after implementing Yangtze Estuary deepwater navigational improvements[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2008, 19(5): 605-612. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2008.05.001 LIU Jie, CHEN Jiyu, XU Zhiyang. River-bed evolution in the braided reach of the south and north passage after implementing Yangtze Estuary deepwater navigational improvements[J]. Advances in Water Science, 2008, 19(5): 605-612. (in Chinese) doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-6791.2008.05.001
[26] 简宏康, 汤立群, 郭传胜, 等. 长江口拦门沙冲淤演变及其机理研究综述[J]. 泥沙研究,2021,46(2):74-80. (JIAN Hongkang, TANG Liqun, GUO Chuansheng, et al. Review of the study on morphological evolution and mechanism of mouth sandbars in the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2021, 46(2): 74-80. (in Chinese) JIAN Hongkang, TANG Liqun, GUO Chuansheng, et al. Review of the study on morphological evolution and mechanism of mouth sandbars in the Yangtze River Estuary[J]. Journal of Sediment Research, 2021, 46(2): 74-80. (in Chinese)


 Email Alerts
Email Alerts RSS
RSS
 下载:
下载: