Scouring study of pile foundation perforated breakwater under regular wave action
-
摘要:
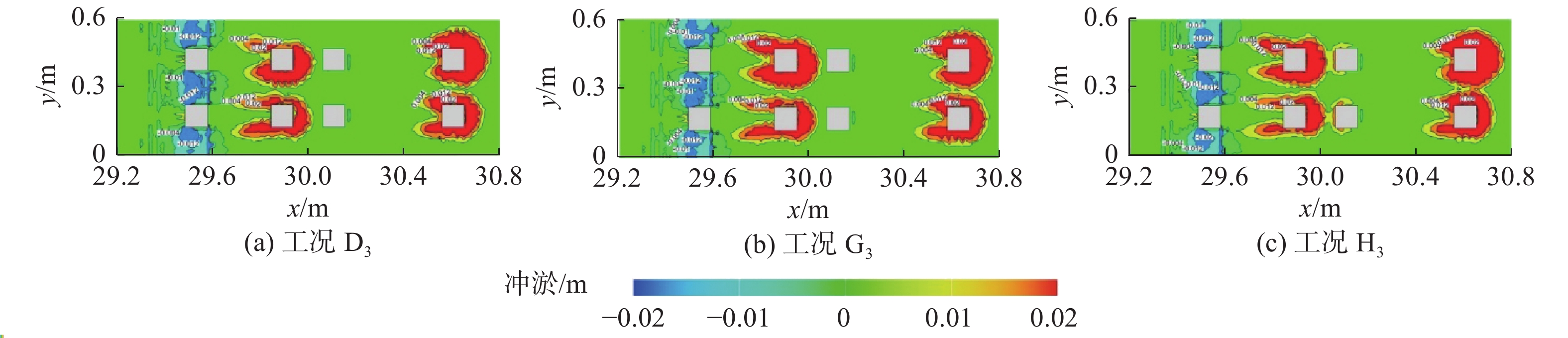
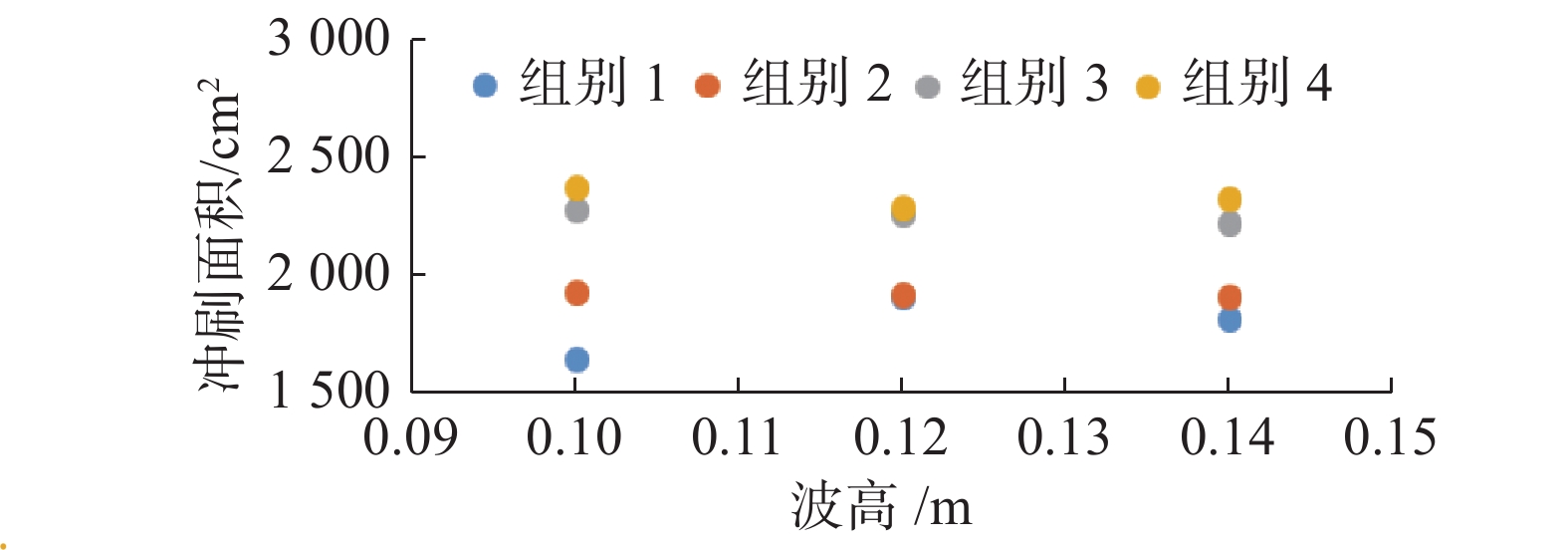
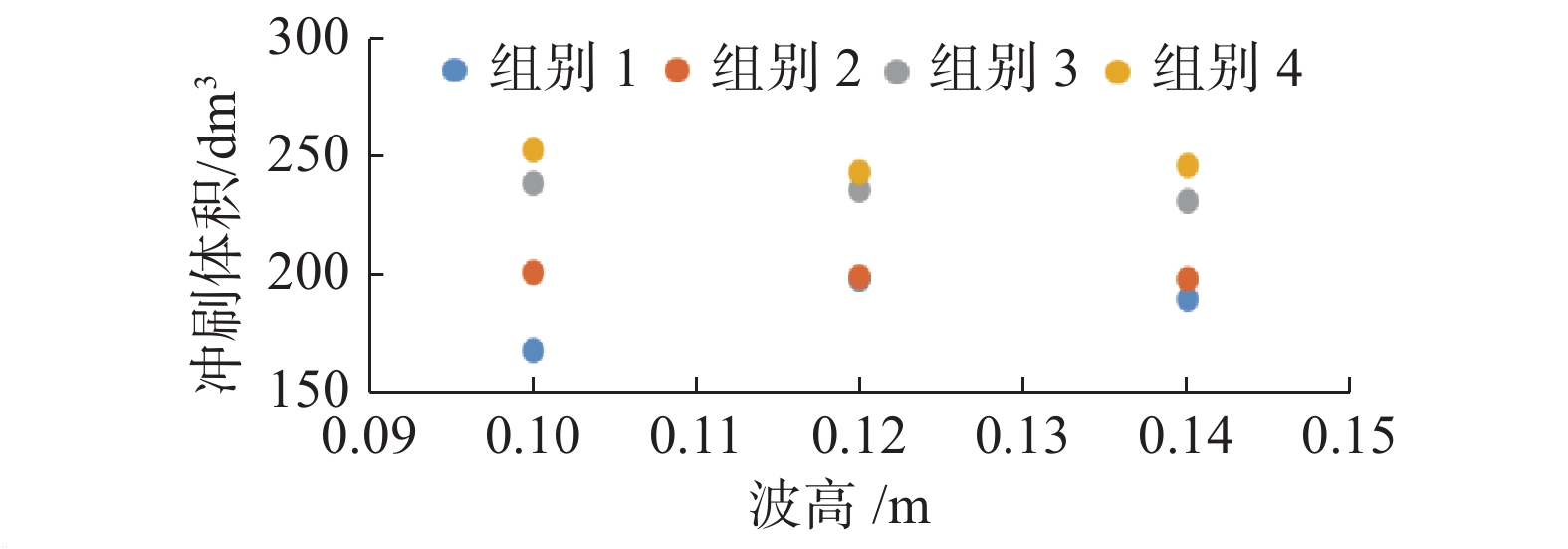
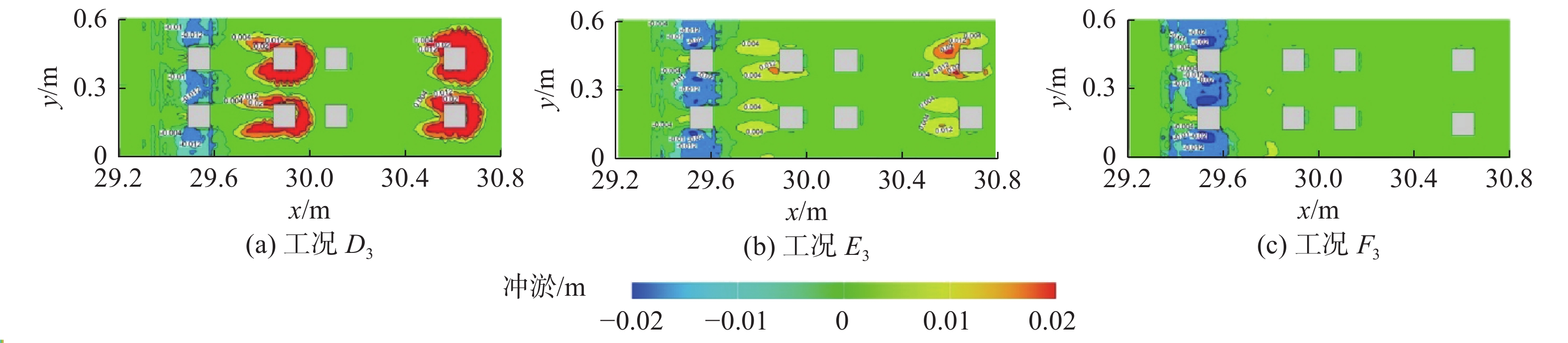
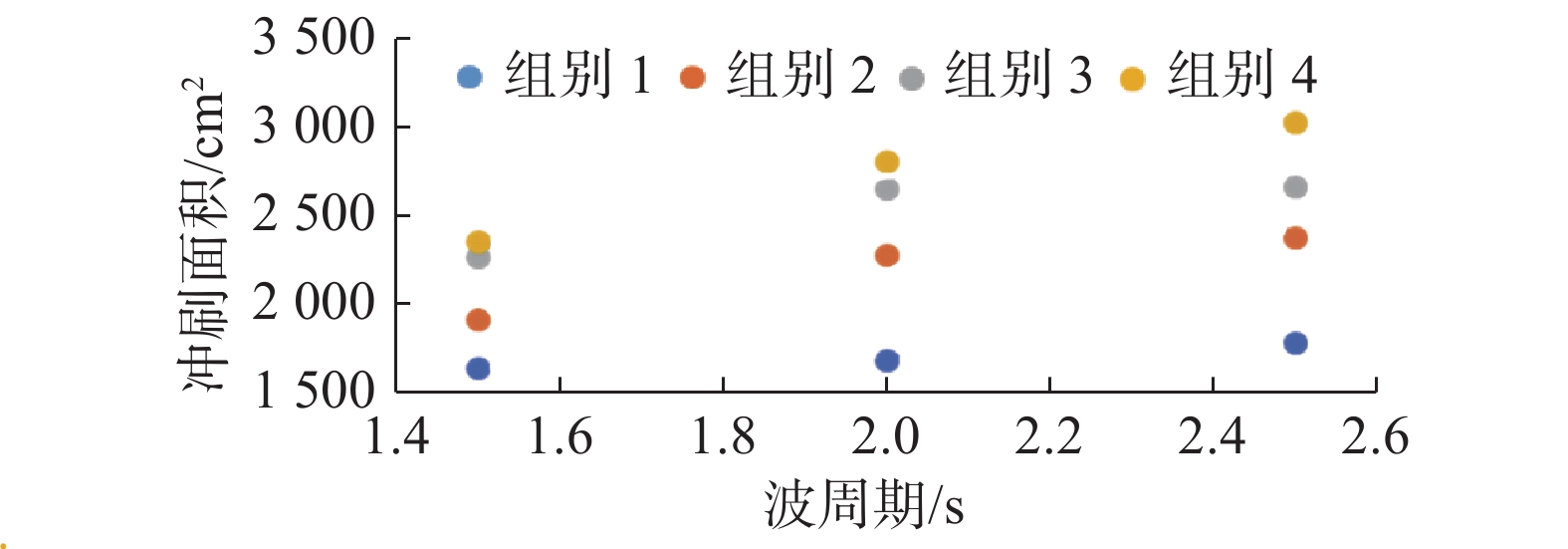
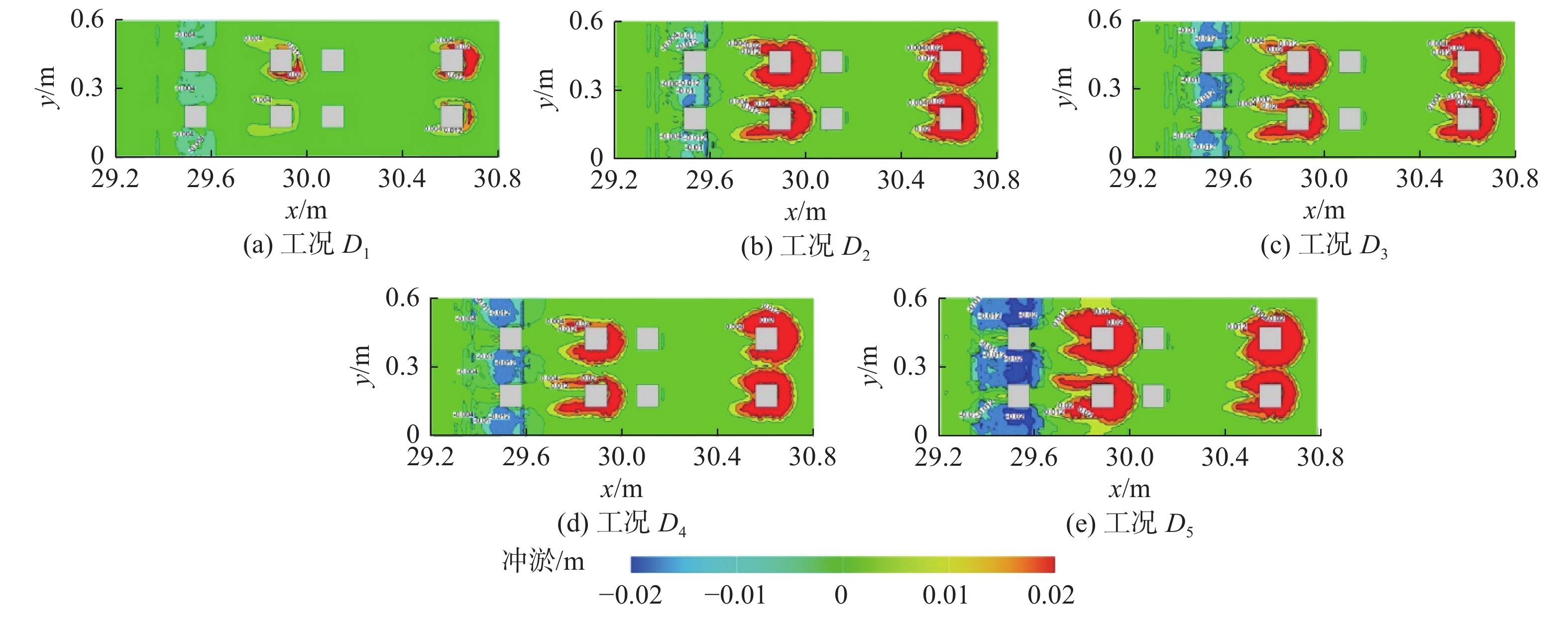
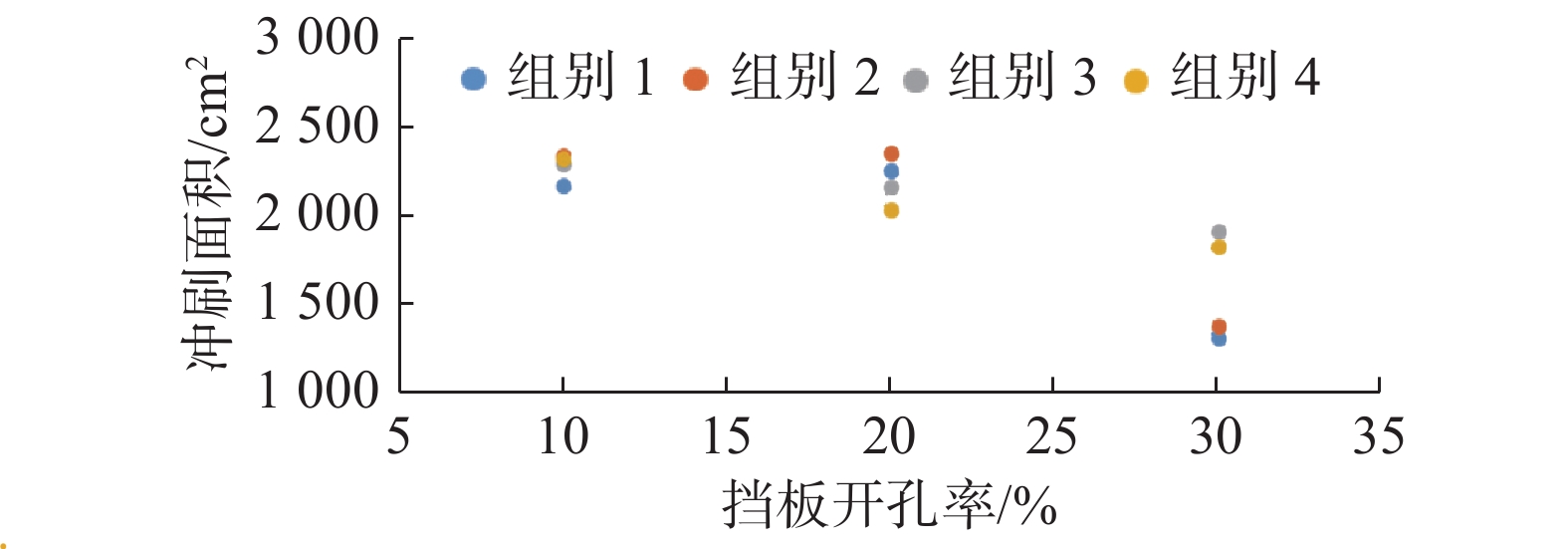
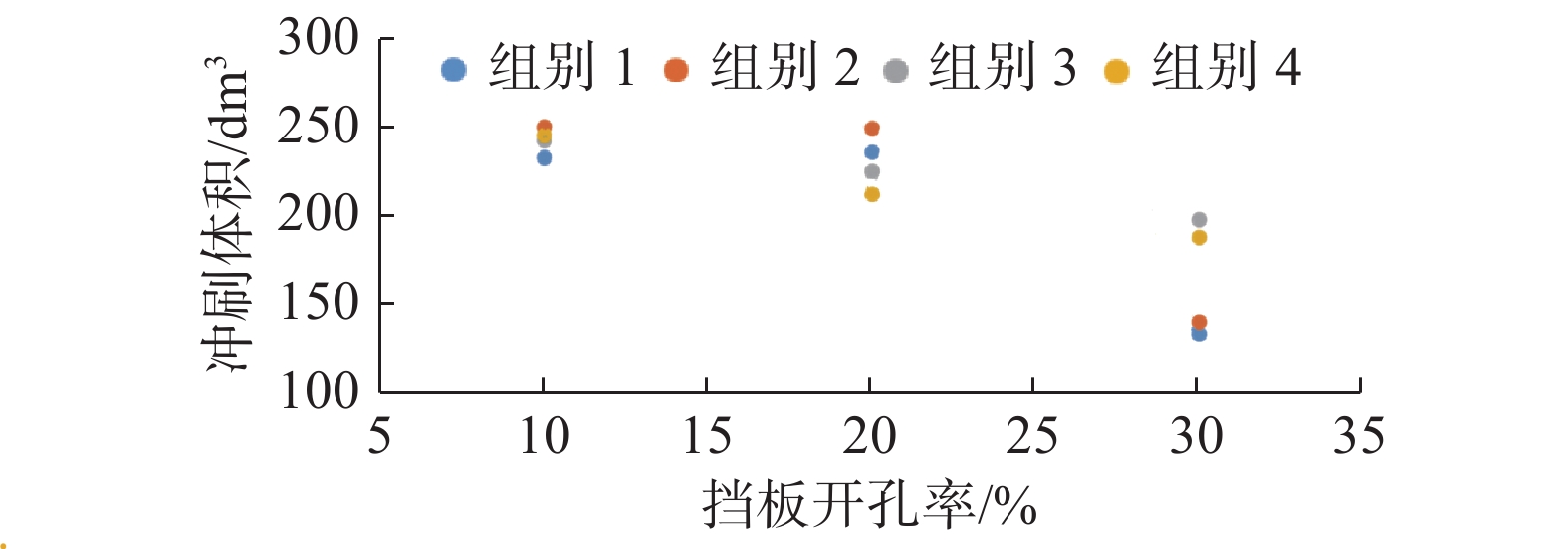
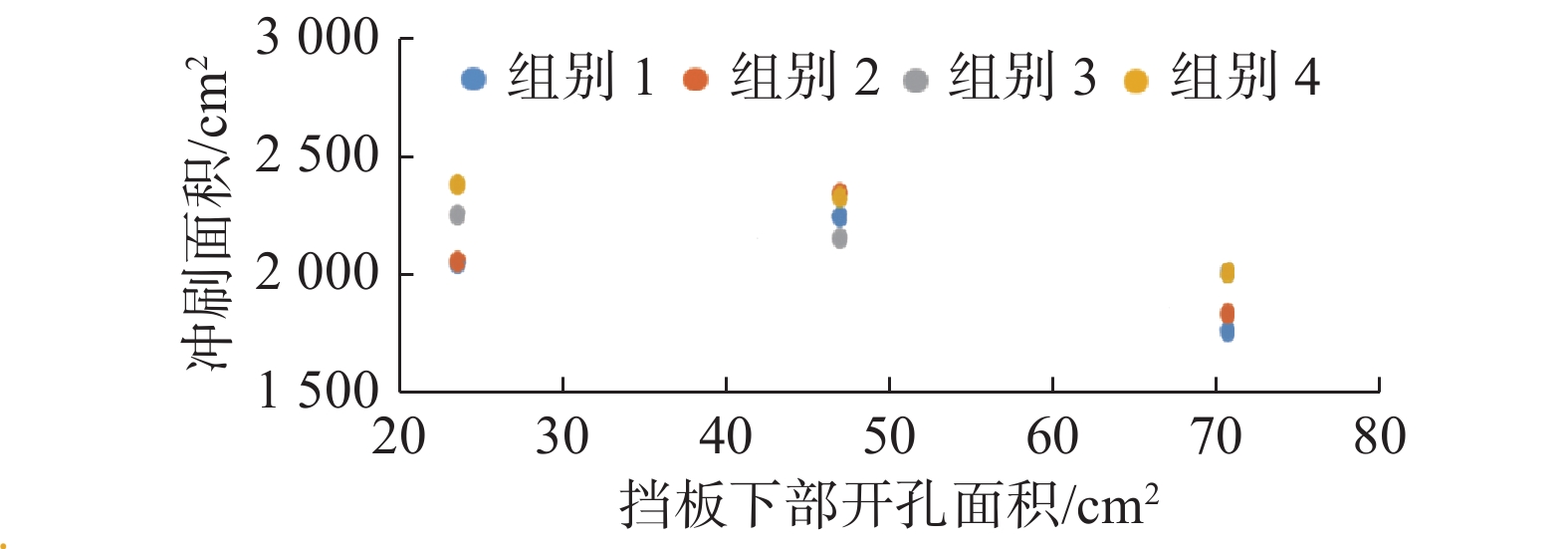
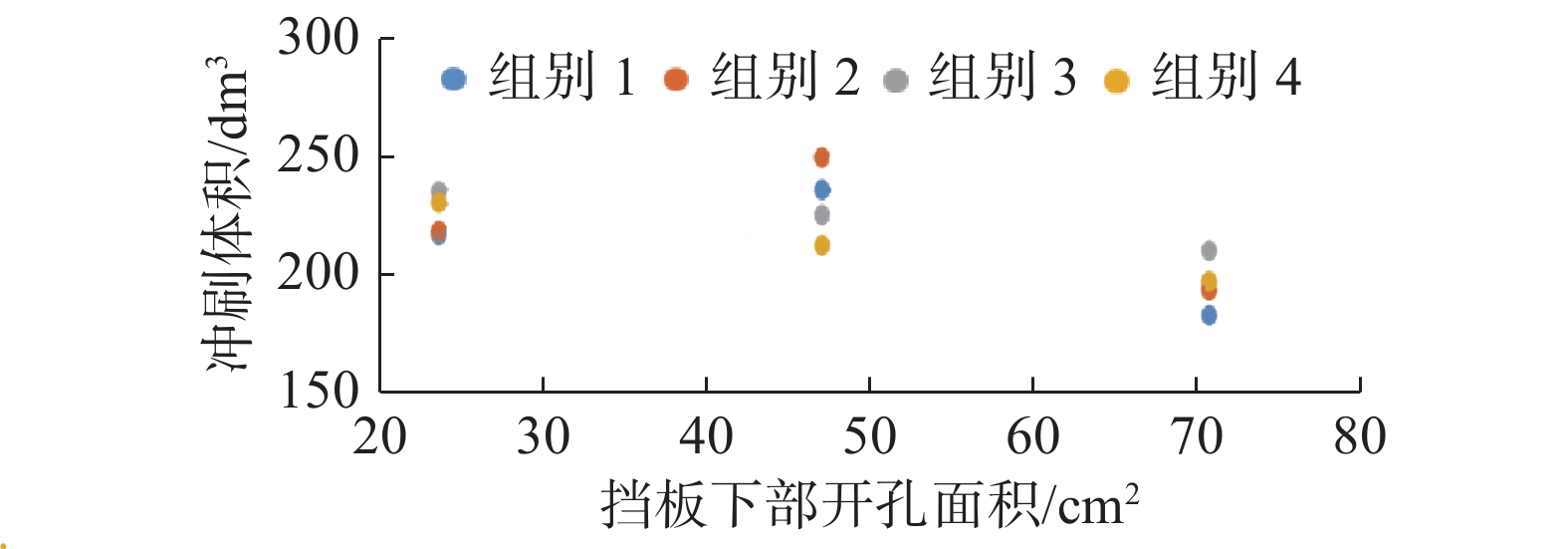
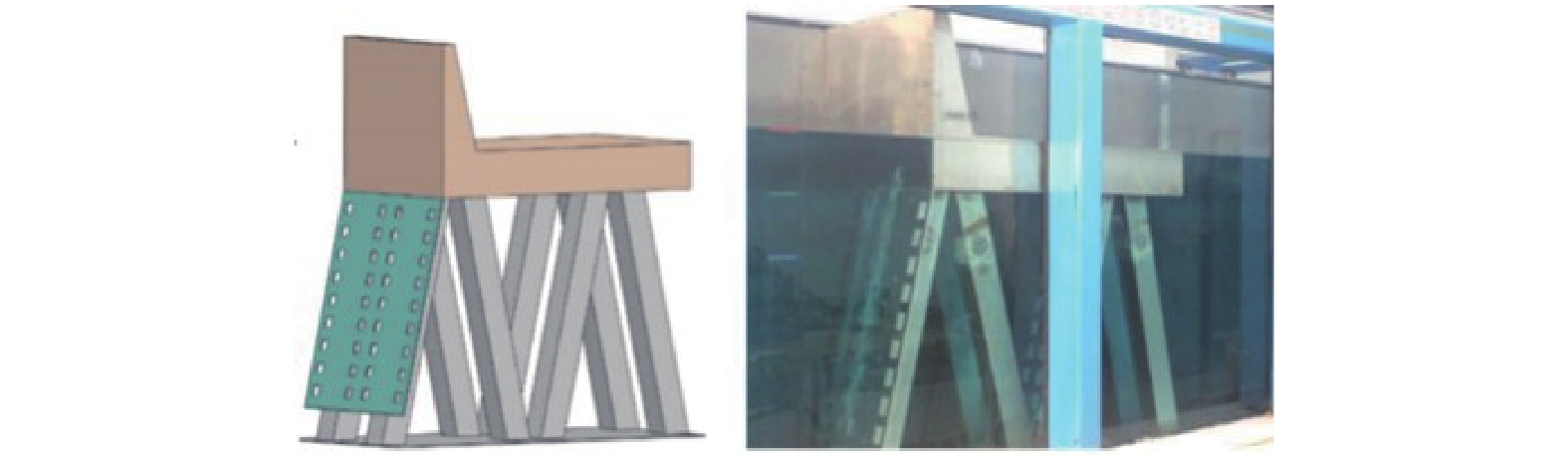
基于FLOW-3D软件,开展了3组波高、3组波周期、5种挡板形式条件下的冲刷模拟试验,分析了不同工况下防波堤结构流场变化、海床冲刷地形变化。研究结果表明:在规则波作用下,波高变化对防波堤结构流场变化及海床冲刷地形变化影响程度较小。波周期则与防波堤结构周围的泥沙冲刷效率呈正相关,且影响程度较大。不同的波周期会导致挡板开孔方式对海床冲刷地形的变化呈现不同的规律,当波周期为1.5 s时,随着挡浪板开孔率的增加、挡板下部面积的增大,冲刷坑面积及体积逐渐减小,且呈线性分布;当波周期为2.0、2.5 s时,冲刷面积及体积呈二次曲线分布。
Abstract:Based on the FLOW-3D software, scour simulation experiments were conducted under the conditions of 3 sets of wave heights, 3 sets of wave periods, and 5 types of baffle forms. The study analyzed the changes in the flow field around the breakwater structure and the changes in seabed scouring topography under different working conditions. The results indicate that under the action of regular waves, the variation in wave height has a minor impact on the changes in the flow field around the breakwater structure and the changes in seabed scouring topography. In contrast, the wave period is positively correlated with the efficiency of sediment scour around the breakwater structure, having a more significant impact. Different wave periods lead to different patterns in the changes in seabed scouring topography due to the way the baffles are opened. When the wave period is 1.5 s, with the increase of the baffle open rate and the enlargement of the area at the bottom of the baffle, the area and volume of the scour pit gradually decrease, displaying a linear distribution; when the wave period is 2.0 and 2.5 s, the area and volume of scouring show a quadratic curve distribution.
-
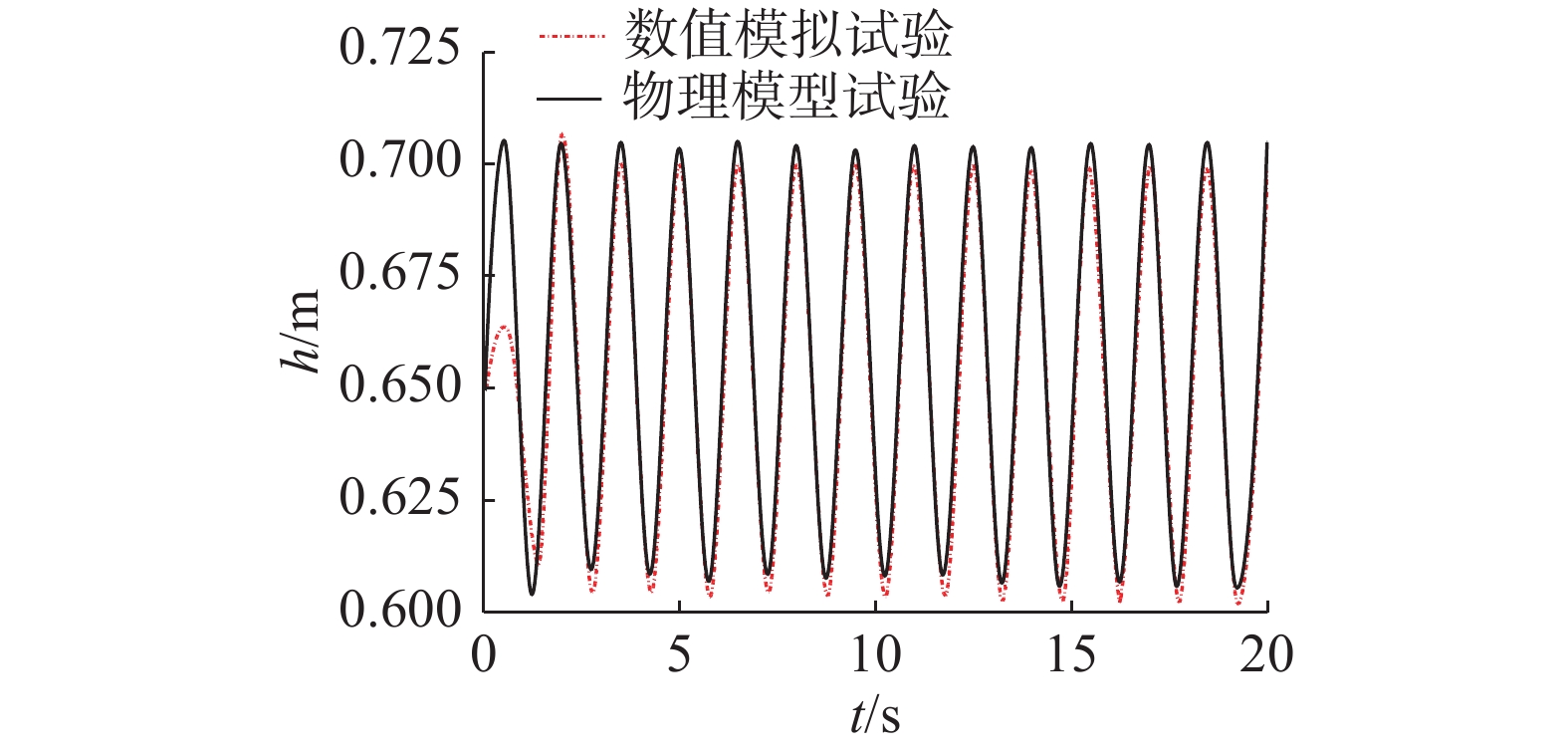
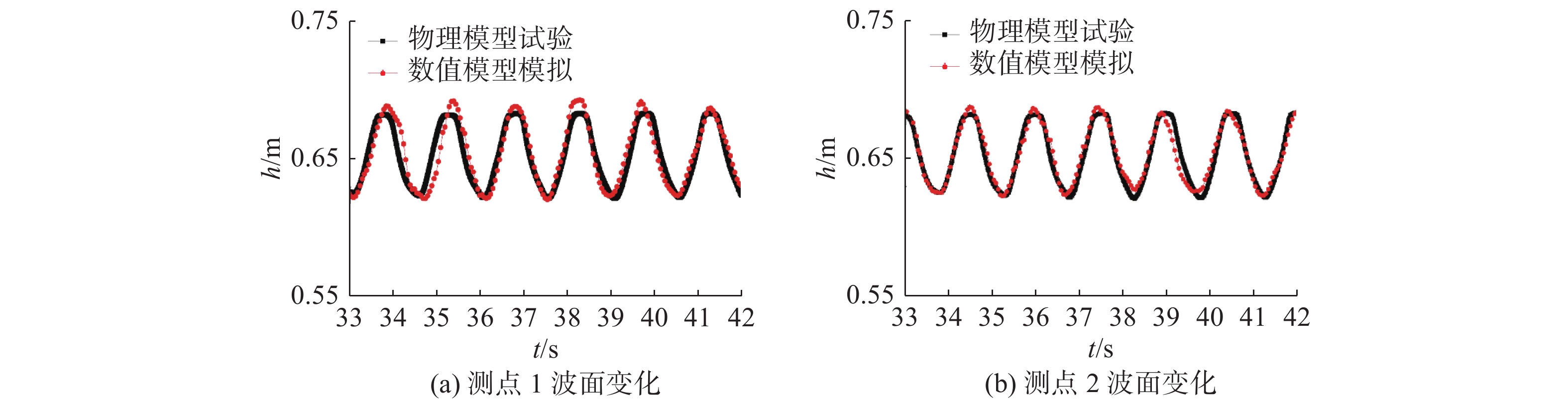
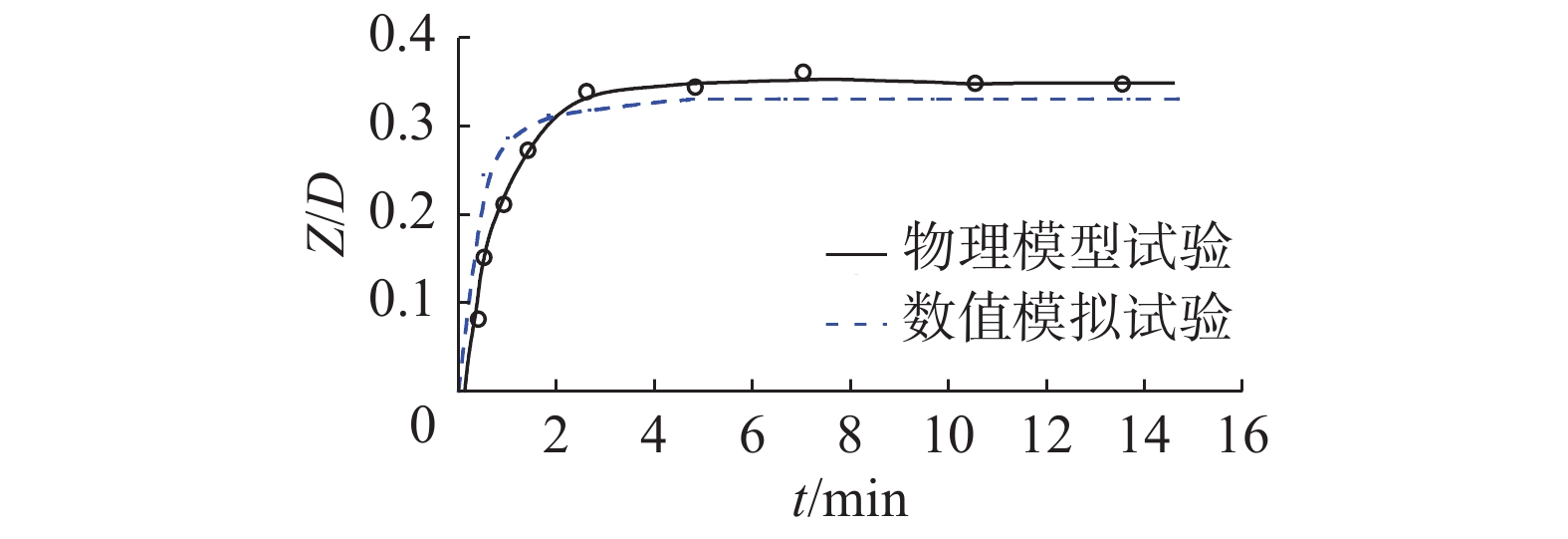
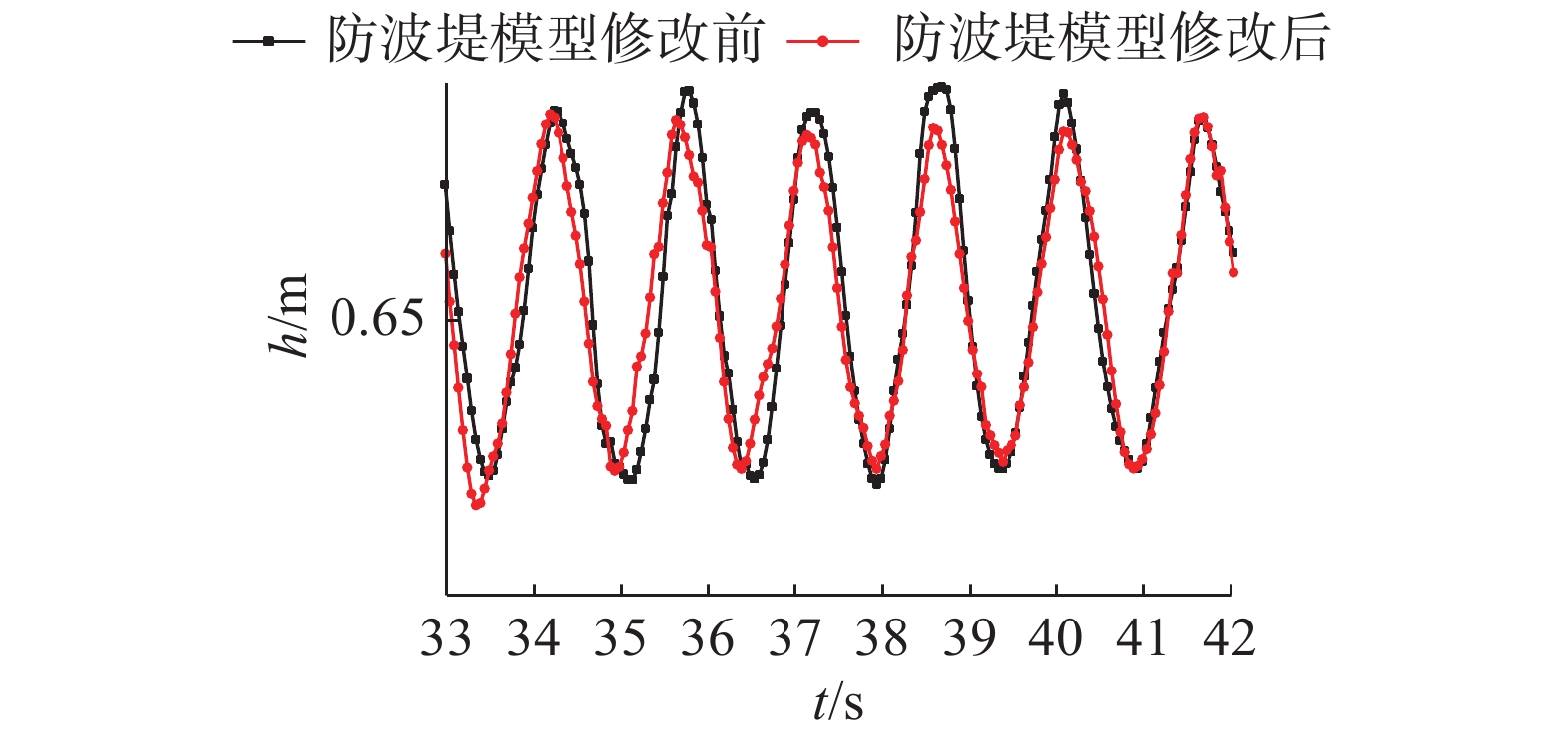
表 1 物理模型试验与数值模拟结果验证
Table 1 Validation of physical model experiment and numerical simulation results
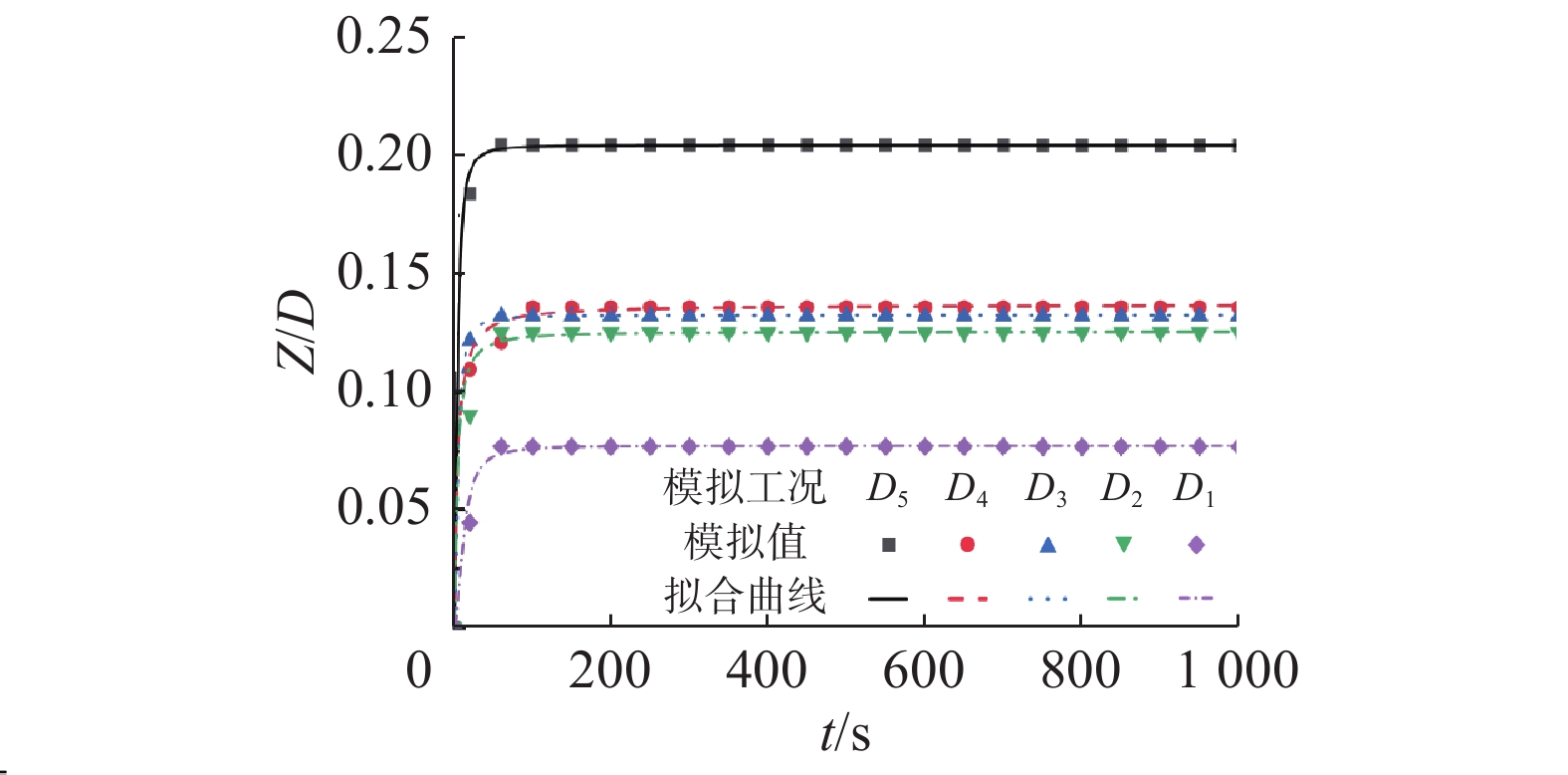
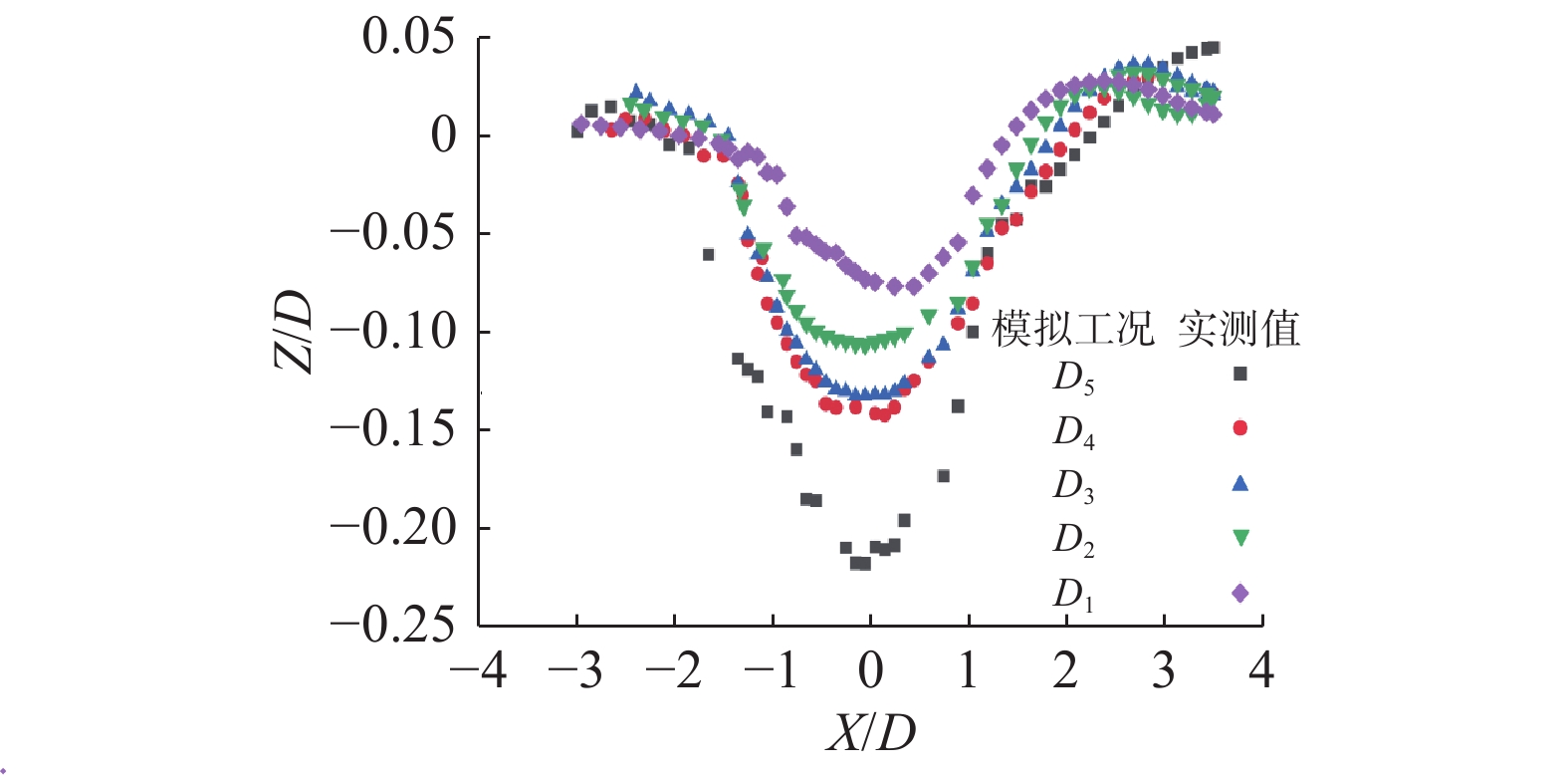
工况组别 验证信息 物理模型结果 数值模型结果 误差/% 工况组别 验证信息 物理模型结果 数值模型结果 误差/% 工况1 Um 0.21 0.22 5.8 工况2 Um 0.31 0.32 4.5 Z/D 0.20 0.19 4.4 Z/D 0.35 0.33 5.4 注:Um为近底层未受扰动的水质点最大水平速度(m/s);Z/D为平衡冲刷深度与桩径的比值。 表 2 波浪作用下数值模拟试验工况
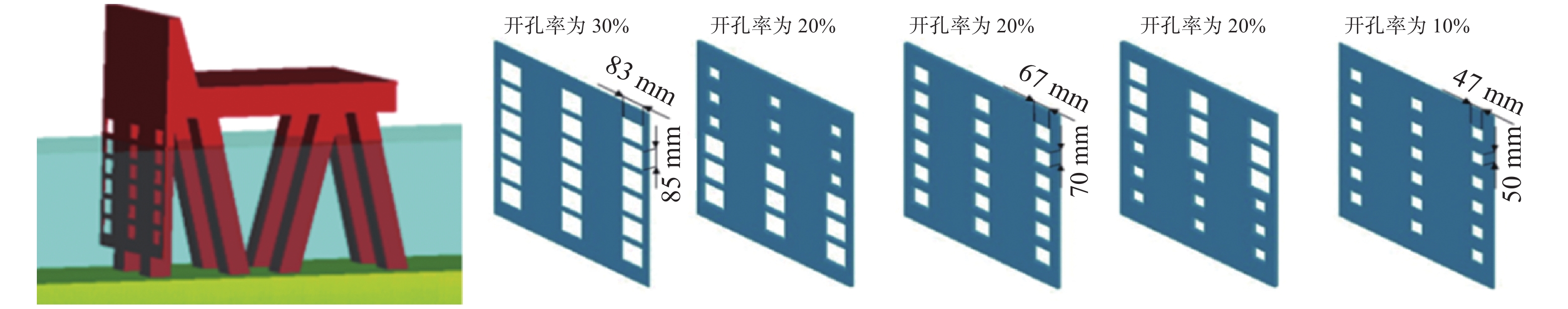
Table 2 Working conditions of numerical simulation experiments under wave action
工况编号 波高/m 波周期/s 挡浪板形式 fKC 工况编号 波高/m 波周期/s 挡浪板形式 fKC D1 0.10 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为30% 1.38 F4 0.10 2.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(30%+10%) 4.33 D2 0.10 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(10%+30%) 1.53 F5 0.10 2.5 挡浪板开孔率为10% 4.97 D3 0.10 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20% 2.06 G1 0.12 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为30% 1.76 D4 0.10 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(30%+10%) 2.88 G2 0.12 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(10%+30%) 1.91 D5 0.10 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为10% 2.12 G3 0.12 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20% 2.22 E1 0.10 2.0 挡浪板开孔率为30% 1.68 G4 0.12 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(30%+10%) 2.94 E2 0.10 2.0 挡浪板开孔率为20%(10%+30%) 2.92 G5 0.12 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为10% 2.79 E3 0.10 2.0 挡浪板开孔率为20% 1.8 H1 0.14 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为30% 0.97 E4 0.10 2.0 挡浪板开孔率为20%(30%+10%) 4.68 H2 0.14 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(10%+30%) 1.03 E5 0.10 2.0 挡浪板开孔率为10% 4.81 H3 0.14 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20% 0.78 F1 0.10 2.5 挡浪板开孔率为30% 3.53 H4 0.14 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(30%+10%) 1.06 F2 0.10 2.5 挡浪板开孔率为20%(10%+30%) 3.46 H5 0.14 1.5 挡浪板开孔率为10% 1.18 F3 0.10 2.5 挡浪板开孔率为20% 5.05 注:无量纲参数fKC(Keulegan-Carpenter数)是影响局部参数的综合因子,$ f_{\mathrm{KC}}={{U}_{\mathrm{m}}{T}}/{{D}} $。 -
[1] 缪银琦, 赵西增, 殷铭简, 等. 带翼排桩式防波堤水动力特性研究[J]. 海洋工程,2024,42(4):86-95. (MIAO Yinqi, ZHAO Xizeng, YIN Mingjian, et al. Research on hydrodynamic characteristics of winged pile-type breakwaters[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2024, 42(4): 86-95. (in Chinese) MIAO Yinqi, ZHAO Xizeng, YIN Mingjian, et al. Research on hydrodynamic characteristics of winged pile-type breakwaters[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2024, 42(4): 86-95. (in Chinese)
[2] 才瀚涛,黄华,苏炜. 椭圆余弦波对V 形防波堤绕射波浪力的解析计算[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2020(5):16-23. (CAI Hantao, HUANG Hua, SU Wei. Analytical calculation of cnoidal wave diffracted force on a V-shaped breakwater[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2020(5): 16-23. (in Chinese) CAI Hantao, HUANG Hua, SU Wei. Analytical calculation of cnoidal wave diffracted force on a V-shaped breakwater[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2020(5): 16-23. (in Chinese)
[3] 李昌良, 蓝晓俊. 水平斜插板透空式防波堤消波性能数值模拟[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2018(4):75-80. (LI Changliang, LAN Xiaojun. Numerical simulation of wave dissipation property of a new-type open breakwater[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2018(4): 75-80. (in Chinese) LI Changliang, LAN Xiaojun. Numerical simulation of wave dissipation property of a new-type open breakwater[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2018(4): 75-80. (in Chinese)
[4] 杜沛霖, 孙昭晨, 梁书秀. 新型直立式透空堤消浪性能数值研究[J]. 海洋工程,2021,39(1):12-20. (DU Peilin, SUN Zhaochen, LIANG Shuxiu. Numerical study on wave dissipation performance of new type vertical permeable breakwater[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2021, 39(1): 12-20. (in Chinese) DU Peilin, SUN Zhaochen, LIANG Shuxiu. Numerical study on wave dissipation performance of new type vertical permeable breakwater[J]. The Ocean Engineering, 2021, 39(1): 12-20. (in Chinese)
[5] 邱大洪, 王学庚. 深水薄板式防波堤的理论分析[J]. 水运工程,1986(4):8-12. (QIU Dahong, WANG Xuegeng. Theoretical analysis of deep-water thin-plate breakwater[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 1986(4): 8-12. (in Chinese) QIU Dahong, WANG Xuegeng. Theoretical analysis of deep-water thin-plate breakwater[J]. Port & Waterway Engineering, 1986(4): 8-12. (in Chinese)
[6] 唐雯, 胡俊, 程永舟, 等. 新型透空组合板式防波堤结构型式及消浪特性分析[J]. 水利水运工程学报,2017(5):37-44. (TANG Wen, HU Jun, CHENG Yongzhou, et al. Analysis of structure and wave dissipation characteristics of a new type of perforated composite plate breakwater[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2017(5): 37-44. (in Chinese) TANG Wen, HU Jun, CHENG Yongzhou, et al. Analysis of structure and wave dissipation characteristics of a new type of perforated composite plate breakwater[J]. Hydro-Science and Engineering, 2017(5): 37-44. (in Chinese)
[7] FANG Z C, XIAO L F, KOU Y F, et al. Experimental study of the wave-dissipating performance of a four-layer horizontal porous-plate breakwater[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2018, 151: 222-233. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2018.01.041
[8] PENG J M, LI K, GU S T, et al. Numerical simulation of the interaction between waves and pile breakwater with horizontal slotted plates[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2023, 287: 115777. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2023.115777
[9] HUANG J J, CHEN G P. Experimental modeling of wave load on a pile-supported wharf with pile breakwater[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 201: 107149. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107149
[10] 侯仲荃, 石进, 王宪业, 等. 空心块体水沙动力及泥沙淤积特性研究[J]. 海洋学报,2022,44(5):124-133. (HOU Zhongquan, SHI Jin, WANG Xianye, et al. Study on flow and sediment dynamics and deposition characteristics of hollow block[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(5): 124-133. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12284/j.issn.0253-4193.2022.5.hyxb202205012 HOU Zhongquan, SHI Jin, WANG Xianye, et al. Study on flow and sediment dynamics and deposition characteristics of hollow block[J]. Haiyang Xuebao, 2022, 44(5): 124-133. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12284/j.issn.0253-4193.2022.5.hyxb202205012
[11] MOJTAHEDI A, BEIRAGH M S, FARAJPOUR I, et al. Investigation on hydrodynamic performance of an environmentally friendly pile breakwater[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2020, 217: 107942. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2020.107942
[12] LU Y X, LIANG B C, YIN Z G, et al. Experimental study on time factor of scour around pile groups[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 261: 112125. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.112125
[13] DU S T, WU G X, ZHU D Z, et al. Experimental study of local scour around submerged square piles in combined waves and current[J]. Ocean Engineering, 2022, 266: 113176. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2022.113176
[14] 王强, 刘睿, 梁丙臣. 倾斜挡浪板式桩基透空型防波堤的消浪性能研究[J]. 海岸工程,2022,41(2):95-104. (WANG Qiang, LIU Rui, LIANG Bingchen. Experimental study on wave-dissipating performance of pile-supported breakwater with perforated inclined wave screen[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2022, 41(2): 95-104. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1002-3682.20220106001 WANG Qiang, LIU Rui, LIANG Bingchen. Experimental study on wave-dissipating performance of pile-supported breakwater with perforated inclined wave screen[J]. Coastal Engineering, 2022, 41(2): 95-104. (in Chinese) doi: 10.12362/j.issn.1002-3682.20220106001
[15] SUMER B M, CHRISTIANSEN N, FREDSØE J. Influence of cross section on wave scour around piles[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 1993, 119(5): 477-495. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1993)119:5(477)
[16] ROULUND A, SUMER B M, FREDSØE J, et al. Numerical and experimental investigation of flow and scour around a circular pile[J]. Journal of Fluid Mechanics, 2005, 534: 351-401. doi: 10.1017/S0022112005004507
[17] FENTON J D. A fifth-order stokes theory for steady waves[J]. Journal of Waterway, Port, Coastal, and Ocean Engineering, 1985, 111(2): 216-234. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-950X(1985)111:2(216)


 Email Alerts
Email Alerts RSS
RSS

 下载:
下载: